Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Electrons are emitted by a hot filament and are accelerated by an electric field, as shown in the figure. The two stops at the left ensure that the electron beam has a uniform cross-section.
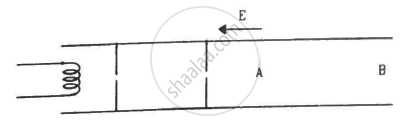
विकल्प
The speed of the electrons is more at B than at A
The electric current is from left to right
The magnitude of the current is larger at B than at A
The current density is more at B than at A
उत्तर
The speed of the electrons is more at B than at A
Let the potentials at A and B be VA and VB.
As potential,
\[E = - \frac{dV}{dr}\]
potential increases in the direction opposite to the direction of the electric field.
Thus, VA < VB
Potential energy of the electrons at points A and B:-
UA = -eVA
UB = -eVB
Thus, UA > UB
Let the kinetic energy of an electron at points A and B be KA and KB respectively.
Applying the principle of conservation of mechanical energy, we get:-
UA + KA = UB + KB
As, UA > UB,
KA < KB
Therefore, the speed of the electrons is more at B than at A.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term drift velocity.
What is its relation with relaxation time?
Write its (‘mobility’ of charge carriers) S.I. unit
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 1.0 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 1.5 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2·5 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 2·7 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3
How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in temperature? Explain.
Why alloys like constantan and manganin are used for making standard resistors?
When electrons drift in a metal from lower to higher potential, does it mean that all the free electrons of the metal are moving in the same direction?
Define relaxation time of the free electrons drifting in a conductor. How is it related to the drift velocity of free electrons? Use this relation to deduce the expression for the electrical resistivity of the material.
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor in terms of relaxation time.
Obtain the expression for the current flowing through a conductor having number density of the electron n, area of cross-section A in terms of the drift velocity vd .
The position-time relation of a particle moving along the x-axis is given by x = a - bt + ct2 where a, band c are positive numbers. The velocity-time graph of the particle is ______.
Metals are good conductor of heat than insulator because
Amount of charge in coulomb required to deposit one gram equivalent of substance by electrolysis is:-
An electric bulb.is rated 220 v and 100 watt power consumed by it when operated on 'no volt is:-
Explain how free electrons in a metal at constant temperature attain an average velocity under the action of an electric field. Hence, obtain an expression for it.
Consider two conducting wires A and B of the same diameter but made of different materials joined in series across a battery. The number density of electrons in A is 1.5 times that in B. Find the ratio of the drift velocity of electrons in wire A to that in wire B.
A potential difference (V) is applied across a conductor of length 'L' and cross-sectional area 'A'.
How will the drift velocity of electrons and the current density be affected if another identical conductor of the same material were connected in series with the first conductor? Justify your answers.
The drift velocity of electrons in a conductor connected to a battery is given by vd = `(−"eE" τ)/"m"`. Here, e is the charge of the electron, E is the electric field, τ is the average time between collisions and m is the mass of the electron.
Based on this, answer the following:
- How does the drift velocity change with a change in the potential difference across the conductor?
- A copper wire of length 'l' is connected to a source. If the copper wire is replaced by another copper wire of the same area of cross-section but of length '4l', how will the drift velocity change? Explain your answer.
