Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.5 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 1.8 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3.
उत्तर
We know that drift velocity, `V_d=1/(nAq)`
I is the current, n is charge density, q is charge of electron and A is cross-section area.
`:.V_d=1.8/(9xx10^28xx2.5xx10^(-7)xx1.6xx10^(-19))`
`V_d=5xx10^(-4) `
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2·5 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 2·7 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3
(a) drift speed
(b) current density
(c) electric current
(d) electric field
On the basis of electron drift, derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms of number density of free electrons and relaxation time. On what factors does resistivity of a conductor depend?
When a current is established in a wire, the free electrons drift in the direction opposite to the current. Does the number of free electrons in the wire continuously decrease?
Electrons are emitted by a hot filament and are accelerated by an electric field, as shown in the figure. The two stops at the left ensure that the electron beam has a uniform cross-section.
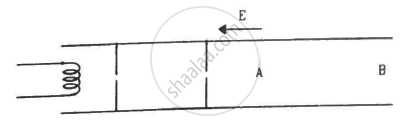
Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Seebeck Effect is caused _____________ .
Obtain the expression for the current flowing through a conductor having number density of the electron n, area of cross-section A in terms of the drift velocity vd .
An electric bulb.is rated 220 v and 100 watt power consumed by it when operated on 'no volt is:-
The identical conductors maintained at same temperature are given potential difference in the ratio 1 : 2. Then the ratio of their drift velocities is ______.
The drift velocity of electrons in a conductor connected to a battery is given by vd = `(−"eE" τ)/"m"`. Here, e is the charge of the electron, E is the electric field, τ is the average time between collisions and m is the mass of the electron.
Based on this, answer the following:
- How does the drift velocity change with a change in the potential difference across the conductor?
- A copper wire of length 'l' is connected to a source. If the copper wire is replaced by another copper wire of the same area of cross-section but of length '4l', how will the drift velocity change? Explain your answer.
