Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a current is established in a wire, the free electrons drift in the direction opposite to the current. Does the number of free electrons in the wire continuously decrease?
उत्तर
No, the number of electrons in the wire remains constant. The electrons that drift and move to the positive terminal of the battery, under the influence of the external electric field, are replaced by the battery in the circuit. As a result, the total number of free electrons in the wire is always constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term drift velocity.
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2·5 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 2·7 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3
The number density of free electrons in a copper conductor is 8.5 × 1028 m−3. How long does an electron take to drift from one end of a wire 3.0 m long to its other end? The area of cross-section of the wire is 2.0 × 10−6 m2 and it is carrying a current of 3.0 A.
(a) drift speed
(b) current density
(c) electric current
(d) electric field
A conductor of length ‘l’ is connected to a dc source of potential ‘V’. If the length of the conductor is tripled by gradually stretching it, keeping ‘V’ constant, how will (i) drift speed of electrons and (ii) resistance of the conductor be affected? Justify your answer.
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor in terms of relaxation time.
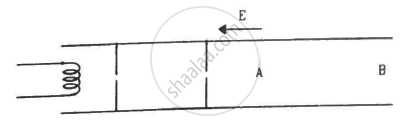
Electrons are emitted by a hot filament and are accelerated by an electric field, as shown in the figure. The two stops at the left ensure that the electron beam has a uniform cross-section.
A current of 1.0 A exists in a copper wire of cross-section 1.0 mm2. Assuming one free electron per atom, calculate the drift speed of the free electrons in the wire. The density of copper is 9000 kg m–3.
Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Seebeck Effect is caused _____________ .
When a current I is set up in a wire of radius r, the drift velocity is vd· If the same current is set up through a wire of radius 2 r, the drift velocity will be:
Metals are good conductor of heat than insulator because
The drift velocity of a free electron inside a conductor is ______
The identical conductors maintained at same temperature are given potential difference in the ratio 1 : 2. Then the ratio of their drift velocities is ______.
Is the momentum conserved when charge crosses a junction in an electric circuit? Why or why not?
The relaxation time τ is nearly independent of applied E field whereas it changes significantly with temperature T. First fact is (in part) responsible for Ohm’s law whereas the second fact leads to variation of ρ with temperature. Elaborate why?
Define relaxation time.
Consider two conducting wires A and B of the same diameter but made of different materials joined in series across a battery. The number density of electrons in A is 1.5 times that in B. Find the ratio of the drift velocity of electrons in wire A to that in wire B.
The drift velocity of electrons in a conductor connected to a battery is given by vd = `(−"eE" τ)/"m"`. Here, e is the charge of the electron, E is the electric field, τ is the average time between collisions and m is the mass of the electron.
Based on this, answer the following:
- How does the drift velocity change with a change in the potential difference across the conductor?
- A copper wire of length 'l' is connected to a source. If the copper wire is replaced by another copper wire of the same area of cross-section but of length '4l', how will the drift velocity change? Explain your answer.
