Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the concept of 'excess demand' in macroeconomics. Also explain the role of 'open market operation' in correcting it.
उत्तर
Excess demand occurs in a situation when aggregate demand is more than aggregate supply corresponding to full employment. It leads to reduction in inventories and inflation in the economy. This situation is considered an inflationary gap—the difference between aggregate demand beyond full employment and aggregate demand at full employment. Aggregate demand is the AD curve and aggregate supply is the AS curve (as shown in the diagram below). While the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect each other, the full employment equilibrium is attained at Point E. OY is the full
employment level of output, and EY is the aggregate demand at full employment level of output. If the aggregate demand increases beyond the full employment level of output from EY to FY, then the economy will have excess demand, i.e. situation of inflationary gap (FY − EY = FE).
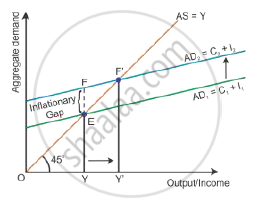
Role of open market operation to curb the excess demand:
Open market operations refer to the sale and purchase of government securities and bonds by the central bank. While controlling inflation, the central bank sells government
securities to the public through the banks. This results in the transfer of a part of bank deposits to the central bank account and reduces credit creation capacity of the commercial banks.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain national income equilibrium through aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Use diagram. Also explain the changes that take place in an economy when the economy is not in equilibrium
Why does consumption curve not start from the origin?
State three measures to reduce inflationary gap.
Explain the role of Repo Rate in reducing the Inflationary gap.
Explain the role of Cash Reserve Ratio in removing an inflationary gap
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money was written by __________.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternatives given below
That part of income, which is not spent on consumption, is called __________.
Match the following Group:
| Group A | Group B | ||
| 1) | Aggregate Supply | a) | Expected receipts |
| 2) | Autonomous Investment | b) | Lord J. M. Keynes |
| 3) | Consumption | c) | Government Investment |
| 4) | A.P.C. | d) | ΔC/ΔY |
| 5) | Investment | e) | C/Y |
| f) | Addition to stock of capital | ||
| g) | Destruction of utility | ||
Distinguish between:
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Answer in detail.
Explain the determinants of aggregate demand.
Answer in detail.
Explain the equilibrium between Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply.
The main component of aggregate demand is ______
In a closed economy, aggregate demand is the sum of ______.
Identify the correctly matched pair from Column A to Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Y = AD | (a) Level of output at full employment |
| (2) Forward Multiplier | (b) Withdrawal of investment decreases income |
| (3) Paradox of Thrift | (c) People save less or same as before |
| (4) Multiplier (k) < 1 | (d) 0 < MPC < 1 |
When aggregate demand is greater than aggregate supply, inventories:
“In an economy Planned spending is more than Planned output”.
Explain its impact on the level of output, income and employment.
With reference to Simple Keynesian model, give the meaning of ex-ante demand.
