Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the working of a LED.
उत्तर
Working: An LED is forward-biased with about 1.2 V to 3.6 V at 12 mA to 20 mA. The majority of carriers electrons from the n-type layer and holes from the p-type layer are injected into the active layer. Electrons cross the junction into the player. In the active player, some of these excess minority carriers, electrons, recombine radiatively with majority carriers, holes, thereby emitting photons. The resulting photon has energy approximately equal to the bandgap of the active layer material. Modifying the bandgap of the active layer creates photons of different energies.

Working on an LED
In the energy band diagram, this recombination is equivalent to a transition of the electron from a higher energy state in the conduction band to a lower energy state in the valence band. The energy difference is emitted as a photon of energy hv.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An LED emits visible light when it's ______.
Choose the correct option.
Solar cell operates on the principle of ______.
Answer in brief.
On which factors does the wavelength of light emitted by a LED depend?
Answer in brief.
Why should a photodiode be operated in reverse biased mode?
State the principle of solar cells.
Answer in brief.
State the uses of the solar cell.
Explain how a Zener diode maintains a constant voltage across a load.
Explain the forward and the reverse characteristic of a Zener diode.
Explain the principle of operation of a photodiode.
State any two special-purpose diodes.
State any two advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode.
Define the dark current of the photodiode. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a photodiode?
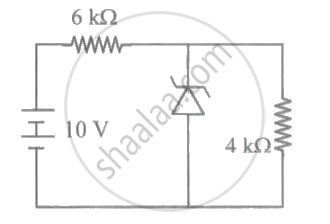
What will be the current flowing through the 6 kΩ resistor in the circuit shown, where the breakdown voltage of the Zener is 6V?
With forward biased mode, the p-n junction diode ______.
With a neat labelled diagram, explain the working of a photodiode. Calculate the wavelength in angstrom at which the emissive power is maximum for a blackbody heated to 3727 °C.
State the factors which control the wavelength of light emitte d by an LED.
Zener breakdown results from breaking of Si-Si covalent bonds in a silicon junction diode due to ______.
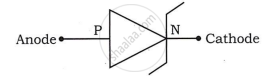
Give the name of the following symbol.
Draw a neat labelled schematic diagram of LED.
Distinguish between light-emitting diode and photo-diode.
What is Avalanche breakdown?
What is a Light Emitting Diode?
Draw Light Emitting Diode circuit symbol.
