Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fill in the blank.
In humans, ------ chromosome is responsible for maleness.
उत्तर
In humans, Y chromosome is responsible for maleness.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name any three parts of the female reproductive system in human beings. Write one function of each.
Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
State the changes that take place in the uterus when Implantation of embryo has occurred
The pituitary hormone which stimulates contraction of uterus during child birth.
State the main function of the Leydig cells
The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus. Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) Mention any two functions of the part labelled 2 in the diagram.
(iii) Explain the significance of the part numbered 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Define the term ‘Gestation’. What is the normal gestational period of the developing human embryo?
(v) Mention the sex chromosomes in a male and female embryo.
A single highly coiled tube where sperms are stored gets concentrated, and mature is known as ______
State the main function of the Sperm duct.
Give biological explanations for The placenta is an important structure for the development of a foetus
What are the organs in humans which produce the gametes?
What are the female sex cells in humans called?
What do the ovaries in a woman produce?
What is the frequency of menstrual cycle in human females (or women)?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The menstrual cycle is controlled by.............
Write the names of male sex hormone?
What is the scientific name of birth canal?
How long does a human baby take to develop before birth?
The germ cell A produced by a person X is round in shape and it fuses with another germ cell B having a long tail and produced by a person Y. The fusion of A and B produces a new cell C. The cell C divides repeatedly and grows inside the organ D of person X to form E in which the body features of the unborn baby are not much developed. E grows further to form F in which the various body features of the unborn baby (like hands, legs, head, eyes, and ears, etc.) can be identified. F grows further and ultimately forms a baby. What are A, B, C, D, E and F? Out of the two persons X and Y, which one is male and which one female?
Explain how the transmission of virus and bacteria diseases be prevented?
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the following parts :
(i) Where the development of egg occurs.
(ii) Where fertilization takes place.
State the role of placenta in the development of embryo.
Give the name:
Methods of family planning.
What is reproduction? List its two types.
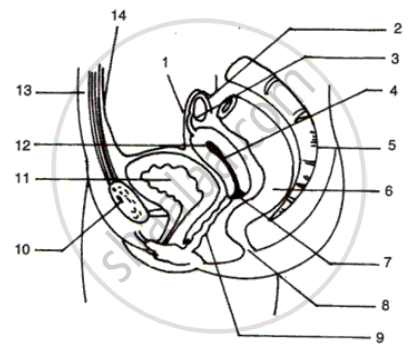
Diagram shows the reproductive system of female human beings:
(i) Name the parts numbered 1 to 14.
(ii) Normally, after how many days does an ovary release an egg?
(iii) Where are the sperms released during coitus?
(iv) What is the role of sperms after their ejaculation in vagina?
(v) What is the function of the organ numbered 5?
(vi) What is the gestation period in human?
Name the following:
Male and Female organs on specific individuals.
Define the following:
Sexual reproduction
Name the organs of the human male reproductive system and state the functions of any two organs.
Identify the given diagram.
Name the parts 1 to 5. 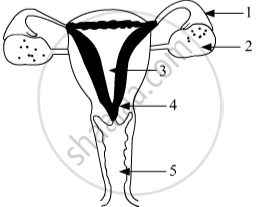
Differentiate on the basis of what is indicated in brackets :
The prostate gland and Cowper’s gland (the nature of secretion)
Name the Following
What does this abbreviation stand for IUD?
Give Technical Term:
What are the age restrictions for marriages by law for boys and girls in India?
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Acrosome
(ii) Ovulation (iii) Sperm (iv) Menopause (v) Implantation (vi) Fertilization (vii) Contraception in males |
(a) Male gamete
(b) Oviduct (c) Uterus (d) Spermatozoa (e) Progesterone (f) Stoppage of the menstrual cycle (g) Sudden change in genes |
Choose the Odd One Out:
Multiple Choice Question:
What will happen if the temperature of the scrotal sacs temporarily goes to about 2°C lower than body temperature?
Gestation period in man
Mention any two changes that are common to both boys and girls in early teenage years.
A zygote is formed by the fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete. The number of chromosomes in the zygote of a human is ______.
