Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fill in the blank.
In humans, ------ chromosome is responsible for maleness.
उत्तर
In humans, Y chromosome is responsible for maleness.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the part where
(i) eggs develop.
(ii) fertilisation takes place.
(iii) fertilised egg gets implanted.
State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
How many pairs of chromosomes are present in human beings? Out of these how many are sex chromosomes?
Name the respective part of human female reproductive system:-
(i) that produces eggs,
(ii) where fusion of eggs and sperm takes place, and
(iii) where zygote gets implanted.
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
What are the different methods of contraception?
Mention the total number of chromosomes along with the sex chromosomes that are present in a human female and a human male. Explain how in sexually producing organisms the number of chromosomes in the progeny remains the same as that of the parents.
Why are testes located outside the abdominal cavity? What is responsible for bringing about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty?
Give technical terms for Thin walled sac of skin which covers the testes
State whether human beings reproduce by sexual method or asexual method.
Where is the female gamete formed in humans?
Which part of the human body produces ova?
What do the testes in a man produce?
For how much time does menstruation last in human females (or women)?
What is the frequency of menstrual cycle in human females (or women)?
What is the name of the narrow opening between the uterus and the vagina.
Name the organs which produce ova (or egg cells) in human females.
Describe the process of fertilisation in humans and development of embryo briefly.
In human females, an event that indicates the onset of reproductive phase is :
(a) growth of body
(b) change in hair pattern
(c) change in voice
(d) menstruation
X and Y are two human beings. The organ A in the reproductive system of X releases a mature gamete B once a month which goes into a tube-like structure C through a funnel-like opening. The organ D in the reproductive system of Y makes and releases gametes E which pass through a duct F and are introduced by an organ of Y, into the body of X. B and E fuse together in C to form a new cell G. The cell G divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells H which gets embedded in the lining of organ I of reproductive system of X where it grows and develops into a baby.
(a) Name (i) organ A, and (ii) gamete B.
(b) Write two names of tube-like structure C.
(c) Name (i) organ D, and (ii) gamete E.
(d) Write two names of duct F.
(e) Name (i) cell G (ii) ball of cells H, and (iii) organ I.
(f) Out of X and Y, which one is (i) male, and (ii) female?
When a fertilised egg E formed in the oviduct of a human female divides repeatedly to form an embryo, the embryo gets implanted in the thick and soft lining of the uterus. After this a disc-like special tissue T develops between the uterus wall and embryo through which all the requirements of the developing embryo (and foetus) are met from the mother's body, The embryo is connected to the tissue T through a string like structure S.
(a) What is the other name of fertilised egg cell E?
(b) What is the name of tissue T?
(c) Name the string-like structure S.
(d) Name two substances which pass from mother's blood to embryo through tissue T and, one type of substance which passes from embryo to mother's blood.
(e) What happens to S when the baby is born? Why?
Given below is a diagram of two systems together in the human body.
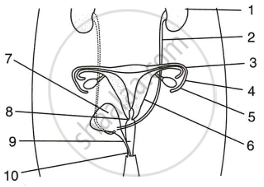 |
- Name the systems.
- Name the parts numbered 1-10.
- Describe the functions of the parts 3, 4, 5 & 6.
- What will happen if the part 3 on both sides gets blocked?
The normal gestation period in humans is:
Write two examples of sexually transmitted diseases caused by virus.
Trace the path of sperms from where they are produced in human body to the exterior.
Choose the correct answer:
First menstrual cycle is known as ___________
Define the following:
Parthenogenesis
The below diagram is of a developing embryo is a mother’s womb:

(i) Write the functions of the placenta, amnion, and umbilical cord.
(ii) How are the waste products of a fetus removed?
(iii) What is the gestation period?
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Acrosome
(ii) Ovulation (iii) Sperm (iv) Menopause (v) Implantation (vi) Fertilization (vii) Contraception in males |
(a) Male gamete
(b) Oviduct (c) Uterus (d) Spermatozoa (e) Progesterone (f) Stoppage of the menstrual cycle (g) Sudden change in genes |
Choose the Odd One Out:
______ is a lytic enzyme released by the sperm.
If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will NOT be transported form ______
Gestation period in man
Mention any two changes that are common to both boys and girls in early teenage years.
