Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Fill in the blank.
In humans, ------ chromosome is responsible for maleness.
Solution
In humans, Y chromosome is responsible for maleness.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the functions of the following organs of reproduction:
a. Ovaries
b. Seminal vesicle and prostate glands
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
State the changes that take place in the uterus when Female gamete/egg is not fertilised
When a cell reproduces, what happens to its DNA?
The pituitary hormone which stimulates contraction of uterus during child birth.
Name the cells that secrete Testosterone
State the main function of the Corpus luteum
The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus. Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) Mention any two functions of the part labelled 2 in the diagram.
(iii) Explain the significance of the part numbered 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Define the term ‘Gestation’. What is the normal gestational period of the developing human embryo?
(v) Mention the sex chromosomes in a male and female embryo.
Give technical terms for Thin walled sac of skin which covers the testes
Where is the female gamete formed in humans?
Where does a fertilised ovum develop into a baby in the human body?
What are the male and female gonads in human beings? Mention their functions.
Mention two functions of human ovaries.
Why is it an advantage for the testes to be situated in the scrotal sac outside the main body cavity? Can you think of one disadvantage?
Which structure in human female is equivalent to the vas deferens in the male?and in what respect the structures are equivalent?
What is the life support system of a fetus?
What is the name of the narrow opening between the uterus and the vagina.
What changes are seen in boys at the time of puberty?
X and Y are two human beings. The organ A in the reproductive system of X releases a mature gamete B once a month which goes into a tube-like structure C through a funnel-like opening. The organ D in the reproductive system of Y makes and releases gametes E which pass through a duct F and are introduced by an organ of Y, into the body of X. B and E fuse together in C to form a new cell G. The cell G divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells H which gets embedded in the lining of organ I of reproductive system of X where it grows and develops into a baby.
(a) Name (i) organ A, and (ii) gamete B.
(b) Write two names of tube-like structure C.
(c) Name (i) organ D, and (ii) gamete E.
(d) Write two names of duct F.
(e) Name (i) cell G (ii) ball of cells H, and (iii) organ I.
(f) Out of X and Y, which one is (i) male, and (ii) female?
Rewrite the terms in the correct order so as to be in a logical sequence.
Implantation, ovulation, child birth, gestation, fertilisation.
The diagram below represents two reproductive cells A and B. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
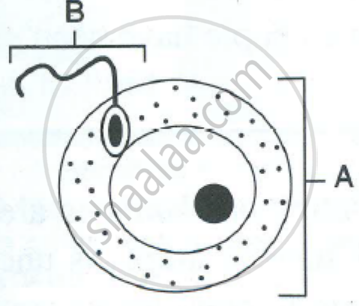 |
- Identify the reproductive cells A and B.
- Name the specific part of the reproductive system where the above cells are produced.
- Where in the female reproductive system do these cells unite?
- Name the main hormones secreted by the (1) ovary (2) testes.
- Name an accessory gland found in the male reproductive system and state the function of its secretion.
Trace the path of sperms from where they are produced in human body to the exterior.
Name the following:
Male and Female organs on specific individuals.
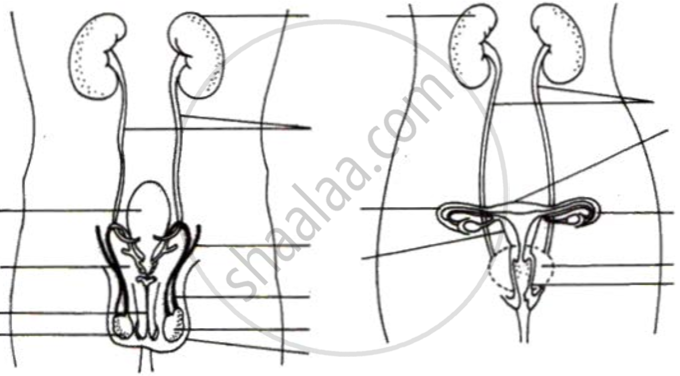
Label the folowing diagram
Identify the given diagram.
Name the parts 1 to 5. 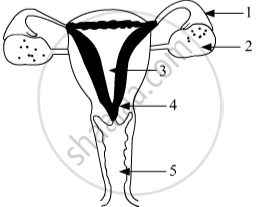
Define the four stages in the uterine cycle.
Give Reasons
At the time of birth, the testes descend into the scrotal sacs.
Name the Following
What does this abbreviation stand for IUD?
State the Location:
Uterus
Choose the Odd One Out:
Choose the Odd One Out:
______ is a lytic enzyme released by the sperm.
Cryptorchidism is a condition where ______.
Freshly released human egg has ______.
The living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from the non-living things on the basis of their ability for ______.
Given below are the events in human reproduction. Write them in correct sequential order.
Insemination, gametogenesis, fertilisation, parturition, gestation, implantation
During adolescence, reproductive phase starts and ______.
