Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the energy, the frequency and the momentum of an X-ray photon of wavelength 0.10 nm.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
उत्तर
Given:
Wavelength of the X-ray photon, λ = 0.1 nm
Speed of light, c = 3 `xx` 108 m/s
(a) Energy of the photon (E) is given by
`E = (hc)/lambda`
⇒ `E = (1242 "eV")/0.1`
⇒ `E = 12420 "eV"`
⇒ `E = 12.42 "keV" ≈ 12.4 "keV"`
(b) Frequency is given by
`v = c/lambda`
⇒`v = (3 xx 10^8)/(0.1 xx 10^-9)`
⇒`v = 3 xx 10^18 "Hz"`
(c) Momentum of the photon (P) is given by
`P = E/c`
⇒`P = (12.4 xx 10^3 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19)/(3 xx 10^8)`
⇒`P = 6.613 xx 10^-24 "kg-m/s" ≈ 6.62 xx 10^-24 "g-m/s"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What role dose infra-red radiation play in physical therapy?
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Name the rays or waves of highest frequency .
How are X-rays produced?
The potential difference applied to an X-ray tube is increased. As a result, in the emitted radiation,
(a) the intensity increases
(b) the minimum wavelength increases
(c) the intensity remains unchanged
(d) the minimum wavelength decreases.
X-ray incident on a material
(a) exerts a force on it
(b) transfers energy to it
(c) transfers momentum to it
(d) transfers impulse to it.
The X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube has a cutoff wavelength of 80 pm. Find the kinetic energy of the electrons hitting the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Name the scientist who discovered radio waves
Name the scientist who discovered Ultraviolet rays
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in increasing order of their frequencies (i.e. begin with the lowest frequency):
Visible light, y rays, X rays, microwaves, radio waves, infrared radiations, and ultraviolet radiation.
Define the term "Intensity" in the photon picture of electromagnetic radiation.
Name any two electromagnetic waves which have a frequency higher than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Give one use of electromagnetic radiation in Microwaves.
Name the radiations used for the detection of fracture in bones.
Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves.
For television broadcasting, the frequency employed is normally
The ozone layer absorbs
Radio waves of constant amplitude can be generated with.
If λv, λx and λm Am represents the wavelength of visible light, x-ray and microwaves respectively, then ______.
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
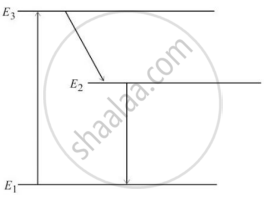
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
