Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point is situated at 7cm and 7·2 cm from two coherent sources. Find the· nature of illumination at the point if wavelength of light is 4000A.
उत्तर
Path difference = 7.2 cm – 7 cm = 0.2 cm
`"Path diffrence "/lambda=0.2/(4000xx10^-8)=5000`
path difference is integral multiple ofλ
∴ It is bright point
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is 'diffraction of light'
In a single slit diffraction pattern, the distance between first minima on the right and first minima on the left of central maximum is 4 mm. The screen on which the pattern is displaced, is 2m from the slit and wavelength of light used is 6000Å. Calculate width of the slit and width of the central maximum.
In the diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 'd' with incident light of wavelength 'λ', at an angle of diffraction θ. the condition for first minimum is ....
(a)`lambda sin theta =d`
(b) `d costheta =lambda`
(c)`d sintheta=lambda`
(d) `lambda cos theta=d`
Explain two types of diffraction of light.
In Fraunhofer diffraction, how is the angular width of the central bright fringe affected when slit separation is increased?
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Two wavelengths of sodium light 590 nm and 596 nm are used, in turn to study the diffraction taking place at a single slit of aperture 2 × 10−4m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.5 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of the first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
In Fraunhofer diffraction, what kind of a source of light is used and where is it situated?
Wavelength of light of frequency 100 Hz is
The penetration of light into the region of geomaterial shadow is called.
The magnifying power of a telescope in normal adjustment is 24, when the length of the telescope tube 1 meter. The focal length of the eye lens is
Which of the following device is used to study the spectra of light?
A polariod (I) is placed in front of a monochromatic source. Another polatiod (II) is placed in front of this polaroid (I) and rotated till no light passes. A third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). In this case, will light emerge from (II). Explain.
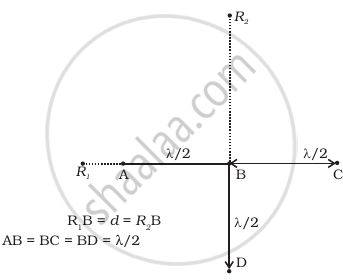
Four identical monochromatic sources A, B, C, D as shown in the (Figure) produce waves of the same wavelength λ and are coherent. Two receiver R1 and R2 are at great but equal distances from B.
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when D is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off?
Draw the graph showing intensity distribution of fringes with phase angle due to diffraction through a single slit. What is the width of the central maximum in comparison to that of a secondary maximum?
Write two points of difference between an interference pattern and a diffraction pattern.
Derive the expression for the angular position of (i) bright and (ii) dark fringes produced in a single slit diffraction.
In the diagram shown, the separation between the slit is equal to 3λ, where λ is the wavelength of the light incident on the plane of the slits. A thin film of thickness 3λ and refractive index 2 has been placed in the front of the upper slit. The distance of the central maxima on the screen from O is ______.
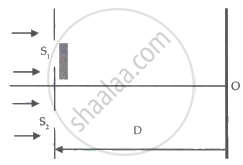
In a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction experiment, how does the angular width of the central maximum change when the slit width is Increased?
Draw a labelled graph showing the variation in intensity of diffracted light with diffracting angle in a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction experiment.
