Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the reaction, \[\ce{A2(g) + B2(g) <=> 2AB(g); \Delta H}\] is -ve.
the following molecular scenes represent differenr reaction mixture. (A-green, B-blue)
| Closed ← |
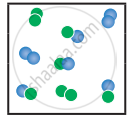 |
 |
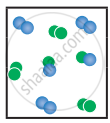 |
| System | At equilibrium | (x) | (y) |
- Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp and (Kc).
- For the reaction mixture represented by scene (x), (y) the reaction proceed in which directions?
- What is the effect of an increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium?
उत्तर
Kc = `(["AB"]^2)/(["A"_2]["B"_2])`; A – green, B – blue
Given that ‘V’ is constant(closed system)
At equilbrium,
Kc = `((-))/((2/"V")(2/"V")) = 16/4 = 4`
Kp = Kc(RT)∆n = 4 (RT)0 = 4
At stage ‘x’,
Q = `((6/"V")^2)/((2/"V")(1/"V")) = 36/2 = 18`
Q > Kc i.e., reverse reaction is favoured.
At stage ‘y’,
Q = `((3/"V")^2)/((3/"V")(3/"V")) = 9/(3 xx 3) = 1`
Kc > Q i.e., forward reaction is favoured.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
K1 and K2 are the equilibrium constants for the reactions respectively.
\[\ce{N2(g) + O2(g) <=>[K1] 2NO(g)}\]
\[\ce{NO(g) + O2(g) <=>[K2] 2NO2(g)}\]
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction \[\ce{NO2(g) <=> 1/2 N2(g) + O2(g)}\]
`"K"_"C"/"K"_"P"` for the reaction,
\[\ce{N2(g) + 3H2(g) <=> 2NH3(g)}\] is
In a chemical equilibrium, the rate constant for the forward reaction is 2.5 × 10-2, and the equilibrium constant is 50. The rate constant for the reverse reaction is,
For the formation of Two moles of SO3(g) from SO2 and O2, the equilibrium constant is K1. The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of one mole of SO3 into SO2 and O2 is
The equilibrium constants of the following reactions are:
\[\ce{N2 + 3H2 <=> 2NH3}\]; K1
\[\ce{N2 + O2 <=> 2NO}\]; K2
\[\ce{H2 + 1/2O2 <=> H2O}\]; K3
The equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction;
\[\ce{2NH3 + 5/2 O2 <=> 2NO + 3H2O}\], will be
Derive a general expression for the equilibrium constant Kp and Kc for the reaction, \[\ce{3H2(g) + N2(g) <=> 2NH3(g)}\].
What is the effect of added Inert gas on the reaction at equilibrium?
One mole of PCl5 is heated in one litre closed container. If 0.6 mole of chlorine is found at equilibrium, Calculate the value of equilibrium constant.
To study the decomposition of hydrogen iodide, a student fills an evacuated 3 litre flask with 0.3 mol of HI gas and allows the reaction to proceed at 500°C. At equilibrium he found the concentration of HI which is equal to 0.05 M. Calculate Kc and Kp.
The equilibrium for the dissociation of XY2 is given as,
\[\ce{2 XY2 (g) <=> 2 XY (g) + Y2 (g)}\]
if the degree of dissociation x is so small compared to one. Show that 2 Kp = PX3 where P is the total pressure and Kp is the dissociation equilibrium constant of XY2.
