Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
To study the decomposition of hydrogen iodide, a student fills an evacuated 3 litre flask with 0.3 mol of HI gas and allows the reaction to proceed at 500°C. At equilibrium he found the concentration of HI which is equal to 0.05 M. Calculate Kc and Kp.
उत्तर
V = 3 L
`["HI"]_"initial" = (0.3 "mol")/(3"L")` 0.1 M
[HI]eq = 0.05 M
\[\ce{2 HI(g) <=> H2(g) + l_2(g)}\]
| HI (g) | H2 (g) | I2 (g) | |
| Initial concentration | 0.1 | - | - |
| Reacted | 0.05 | - | - |
| Equilibrium concentration | 0.05 | 0.025 | 0.025 |
`"K"_"C" =(["H"_2]["I"_2])/(["HI"]^2)`
`= (0.025 xx 0.025)/(0.05 xx 0.05)` = 0.25
Kp = Kc(RT)(∆ng)
∆ng = 2 – 2 = 0
Kp = 0.25(RT)0
Kp = 0.25.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
K1 and K2 are the equilibrium constants for the reactions respectively.
\[\ce{N2(g) + O2(g) <=>[K1] 2NO(g)}\]
\[\ce{NO(g) + O2(g) <=>[K2] 2NO2(g)}\]
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction \[\ce{NO2(g) <=> 1/2 N2(g) + O2(g)}\]
In the equilibrium,
\[\ce{2A(g) <=> 2B(g) + C2(g)}\]
the equilibrium concentrations of A, B and C2 at 400 K are 1 × 10–4 M, 2.0 × 10–3 M, 1.5 × 10–4 M respectively. The value of KC for the equilibrium at 400 K is
In which of the following equilibrium, Kp and Kc are not equal?
In a chemical equilibrium, the rate constant for the forward reaction is 2.5 × 10-2, and the equilibrium constant is 50. The rate constant for the reverse reaction is,
The equilibrium constants of the following reactions are:
\[\ce{N2 + 3H2 <=> 2NH3}\]; K1
\[\ce{N2 + O2 <=> 2NO}\]; K2
\[\ce{H2 + 1/2O2 <=> H2O}\]; K3
The equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction;
\[\ce{2NH3 + 5/2 O2 <=> 2NO + 3H2O}\], will be
For the reaction, \[\ce{A2(g) + B2(g) <=> 2AB(g); \Delta H}\] is -ve.
the following molecular scenes represent differenr reaction mixture. (A-green, B-blue)
| Closed ← |
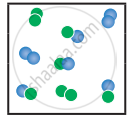 |
 |
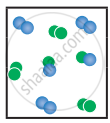 |
| System | At equilibrium | (x) | (y) |
- Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp and (Kc).
- For the reaction mixture represented by scene (x), (y) the reaction proceed in which directions?
- What is the effect of an increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium?
Derive a general expression for the equilibrium constant Kp and Kc for the reaction, \[\ce{3H2(g) + N2(g) <=> 2NH3(g)}\].
1 mol of CH4, 1 mole of CS2 and 2 mol of H2S are 2 mol of H2 are mixed in a 500 ml flask. The equilibrium constant for the reaction Kc = 4 x 10-2 mol2 lit-2. In which direction will the reaction proceed to reach equilibrium?
At particular temperature Kc = 4 × 10-2 for the reaction, \[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]. Calculate the Kc for the following reaction.
\[\ce{2H2S (g) <=> 2H2 (g) + S2 (g)}\]
At particular temperature Kc = 4 × 10-2 for the reaction, \[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]. Calculate the Kc for the following reaction.
\[\ce{3H2S (g) <=> 3H2 (g) + 3/2 S2 (g)}\]
