Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
At particular temperature Kc = 4 × 10-2 for the reaction, \[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]. Calculate the Kc for the following reaction.
\[\ce{2H2S (g) <=> 2H2 (g) + S2 (g)}\]
उत्तर
KC = 4 x 10-2 for the reaction
\[\ce{H2S (g) <=> H2(g) +1/2 S2(g)}\]
`"K"_"C" = (["H"_2]["S"_2]^(1/2))/(["H"_2"S"]) = 4 xx 10^-2`
For the reaction,
\[\ce{2H2S (g) <=> 2H2 (g) + S2 (g)}\]
`"K"_"C" = (["H"_2]^2["S"_2]^(1/2))/(["H"_2"S"]^2) = (4 xx 10^-2)^2`
= 16 × 10-4
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the equilibrium,
\[\ce{2A(g) <=> 2B(g) + C2(g)}\]
the equilibrium concentrations of A, B and C2 at 400 K are 1 × 10–4 M, 2.0 × 10–3 M, 1.5 × 10–4 M respectively. The value of KC for the equilibrium at 400 K is
For the reaction \[\ce{AB(g) <=> A(g) + B(g)}\], at equilibrium, AB is 20 % dissociated at a total pressure of P, the equilibrium constant Kp is related to the total pressure by the expression
The values of Kp1 and Kp2; for the reactions,
X ⇌ Y + Z,
A ⇌ 2B are in the ratio 9 : 1 if degree of dissociation of X and A be equal then total pressure at equilibrium P1, and P2 are in the ratio
In a chemical equilibrium, the rate constant for the forward reaction is 2.5 × 10-2, and the equilibrium constant is 50. The rate constant for the reverse reaction is,
For the formation of Two moles of SO3(g) from SO2 and O2, the equilibrium constant is K1. The equilibrium constant for the dissociation of one mole of SO3 into SO2 and O2 is
For a given reaction at a particular temperature, the equilibrium constant has a constant value. Is the value of Q also constant? Explain.
What is the relation between Kp and Kc? Given one example for which Kp is equal to Kc.
For the reaction, \[\ce{A2(g) + B2(g) <=> 2AB(g); \Delta H}\] is -ve.
the following molecular scenes represent differenr reaction mixture. (A-green, B-blue)
| Closed ← |
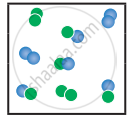 |
 |
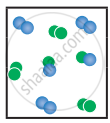 |
| System | At equilibrium | (x) | (y) |
- Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp and (Kc).
- For the reaction mixture represented by scene (x), (y) the reaction proceed in which directions?
- What is the effect of an increase in pressure for the mixture at equilibrium?
Derive a general expression for the equilibrium constant Kp and Kc for the reaction, \[\ce{3H2(g) + N2(g) <=> 2NH3(g)}\].
For the reaction
\[\ce{SrCO3(s) <=> SrO(s) + CO2(g)}\]
the value of equilibrium constant Kp = 2.2 × 10-4 at 1002 K. Calculate Kc for the reaction.
