Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give a reason for the following.
Nitric acid in the dilute form is not used in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from metals.
उत्तर
Nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent and nascent oxygen formed oxidises hydrogen produced to water.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the chemicals required to prepare hydrogen gas in the laboratory.
Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen.
How would you show that hydrogen is a non-supporter of combustion?
Multiple Choice Question
In metal activity series the more reactive metals are at
FILL IN THE BLANK
........................ zinc is preferred over pure zinc in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen.
Name the impurities present in hydrogen prepared in the laboratory.
How can these impurities be removed?
Under what conditions can hydrogen be made to combine with chlorine?
Name the products and write the equation for the reaction.
Give reason:
Apparatus for laboratory preparation of hydrogen should be airtight and away from a naked flame.
How would you show that hydrogen is lighter than air?
Give reason for the following:
Copper does not displace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid, but zinc does.
Complete and balance the equation:
[Laboratory method]
By action of dilute acid on zinc
Zinc - Zn + 2HCl → _____ + _____ [g]
In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc and dil. acid. Give a reason for the following:
The complete apparatus is air-tight.
In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc and dil. acid. Give a reason for the following:
Dilute nitric acid is not preferred as the reactant acid.
Name the following.
A gaseous reducing agent which is basic in nature.
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard laboratory method.
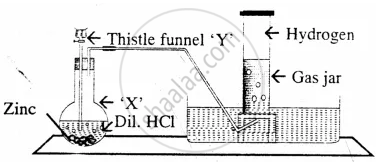
State what difference will be seen if pure zinc is added in the distillation flask ‘X’ instead of granulated zinc.
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard laboratory method.

Name a solution which absorbs the impurity – `"H"_2"S"`
