Advertisements
Chapters
2: Chemical Changes & Reactions
3: Water
4: Atomic Structure & Chemical Bonding
5: The Periodic Table
▶ 6: Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen
7: Study Of Gas Laws
8: Atmospheric Pollution
9: Practical Chemistry
![Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen - Shaalaa.com](/images/simplified-icse-chemistry-english-class-9_6:15cbe1f7c39e424a9ab3e108260ad612.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CISCE Viraf J. Dalal for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9.
Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 6 Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Equation Worksheet
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of active metals - cold water
Potassium- K + H2O → ______+ ______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of active metals - cold water
Sodium - 2Na + 2H2O → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of active metals - cold water
Calcium - Ca + H2O → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with steam
Magnesium - Mg + H2O → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with steam
Aluminium - 2Al + 3H2O → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with steam
Zinc - Zn + H2O → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with steam
Iron - 3Fe + 4H2O ⇌ ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with dilute acids
Magnesium - Mg + 2HCl → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with dilute acids
Aluminium - 2Al + 3H2SO4 → ______+ _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with dilute acids
Zinc - Zn + 2HCl → ______ + _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals with dilute acids
Iron - Fe + 2HCl → ______ + _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals - alkali [conc. soln.]
Zinc - Zn + 2NaOH → ______ + _______ [g]
Zn + 2KOH → ____ + _____ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals - alkali [conc. soln.]
Lead - Pb + 2NaOH → ______ + _______ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[General method]
Reactions of metals - alkali [conc. soln.]
Aluminium - 2Al + 2NaOH + 2H2O → ______ + _______ [g]
2Al + 2KOH + 2H2O → _____ + _____ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[Laboratory method]
By action of dilute acid on zinc
Zinc - Zn + 2HCl → _____ + _____ [g]
Complete and balance the equation:
[Industrial Method - Bosch process]
- Step I - Production of water gas -
\[\ce{C + H2O->[1000°C]}\] [____ + ____] - Δ - Step II - Reduction of steam to hydrogen by carbon monoxide
\[\ce{CO + H2 + H2O->[450°C][Fe2O3]}\] _____ + ____ [g] - Step III - Removal of unreacted carbon dioxide and carbon monoxidefrom the above mixture
KOH + CO2 → _________ + ______
CuCl + CO + 2H2O → _______
Complete and balance the equation:
[Industrial Method - Bosch process]
- Step I - Production of water gas -
\[\ce{C + H2O->[1000°C]}\] [____ + ____] - Δ - Step II - Reduction of steam to hydrogen by carbon monoxide
\[\ce{CO + H2 + H2O->[450°C][Fe2O3]}\] _____ + ____ [g] - Step III - Removal of unreacted carbon dioxide and carbon monoxidefrom the above mixture
KOH + CO2 → _________ + ______
CuCl + CO + 2H2O → _______
Complete and balance the equation:
[Industrial Method - Bosch process]
- Step I - Production of water gas -
\[\ce{C + H2O->[1000°C]}\] [____ + ____] - Δ - Step II - Reduction of steam to hydrogen by carbon monoxide
\[\ce{CO + H2 + H2O->[450°C][Fe2O3]}\] _____ + ____ [g] - Step III - Removal of unreacted carbon dioxide and carbon monoxidefrom the above mixture
KOH + CO2 → _________ + ______
CuCl + CO + 2H2O → _______
Complete and balance the equation:
Conversion of hydrogen to -
Water - 2H2 + O2 → ________
Complete and balance the equation:
Conversion of hydrogen to -
Hydrogen chloride - H2 + Cl2 → ________
Complete and balance the equation:
Conversion of hydrogen to -
Ammonia - N2 + 3H2 ⇌ ______
Complete and balance the equation:
Conversion of hydrogen to -
Hydrogen sulphide - H2 + S → ________
Complete and balance the equation:
Hydrogen in metallurgy - reduction of
Zinc oxide - ZnO + H2 → ________ + ______
Complete and balance the equation:
Hydrogen in metallurgy - reduction of
Iron [III] oxide - Fe2O3 + 3H2 → ________ + ______
Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 6 Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Exercise
Name an element whsich reacts violently with water at room temperature.
What do the following symbols [or formula] denote : 2H ; H2 ; H+. [two atoms, molecule, ion]
Write a correctly balanced equation for the following “word equation”:
calcium + water → calcium hydroxide + hydrogen
When steam is passed over red-hot iron, magnetic oxide of iron and hydrogen are obtained. “The reaction between steam and red-hot iron is a Reversible Reaction.” What is meant by this statement.
How can you obtain hydrogen from sodium hydroxide [not by electrolysis].
Write balanced equation for the following reaction:
magnesium + dil. hydrochloric acid → ___
Name a gas which burns in air or oxygen forming water.
Write correctly balanced equation for the following:
When steam is passed over red hot iron.
Explain the following:
Two jars of H2 are collected – “one burns quietly and the other does not”.
Write correctly the balanced equation for the following:
‘When zinc filings are added to a concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide’.
Describe one chemical test applied to the following gases, which would enable you to distinguish between them :‘carbon monoxide and hydrogen’.
Write down the “word equation” for the following reaction:
sodium hydroxide solution + zinc → ?
Explain briefly how hydrogen is manufactured on a large scale, from steam.
State the products of the reaction “when steam is passed over red-hot iron”.
How can you obtain hydrogen from a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide?
What do you observe when a piece of sodium is dropped into cold water?
Give reason for the following:
Though hydrogen is lighter than air it cannot be collected by downward displacement of air.
Complete the following word equation:
Sodium hydroxide + zinc → hydrogen + _________
Complete the following word equation:
Calcium + water → calcium hydroxide + _________
How would you obtain ‘hydrogen from sodium hydroxide’ solution other than by electrolysis?
Complete and balance the following equations:
Al + NaOH + ____ → ____ + ____
What do the following symbols represent : 2H and H2.
Write balanced equation of the reaction in the preparation of : hydrogen from a solution of potassium hydroxide [other than by electrolysis].
Describe briefly, with equations, the Bosch Process for the large scale production of hydrogen.
Account for the following fact:
Though lead is above hydrogen in the activity series, it does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilutes sulphuric acid.
Account for the following fact:
Potassium and sodium are not used to react with dilute ‘hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen.
Place the metals calcium, iron, magnesium and sodium in order of their activity with water, placing the most active first. Write the equation for each of the above metals which react with Water.
Why is copper not used to prepare hydrogen by the action of dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid on the metal, [copper [Cu] below hydrogen – no reaction]
Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 6 Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Additional Questions
State the electronic configuration of hydrogen [at. no. 1].e
Give a reason why hydrogen can be placed in group 1 [1A] and group 17 [VIIA] of the periodic table.
Give the general group characteristic applied to hydrogen with respect to similarity in properties of hydrogen with alkali metals of group 1 [IA]. With special reference to valency electrons & ion formation.
Give the general group characteristic applied to hydrogen with respect to similarity in properties of hydrogen with halogens of group 17 [VIIA].
With special reference to valency electrons & ion formation.
How did the name ‘hydrogen’ originate? How does hydrogen occur in the combined state?
Give balanced equation for obtaining hydrogen from cold water using a monovalent active metal.
Give balanced equation for obtaining hydrogen from cold water using a divalent active metal.
Give a balanced equation for obtaining hydrogen from?
Boiling water using a divalent metal
Give a balanced equation for obtaining hydrogen from?
Steam using a trivalent metal
Give a balanced equation for obtaining hydrogen from?
Steam using a metal – and the reaction is reversible.
State why hydrogen is not prepared in the laboratory by the action of sodium with cold water.
State why hydrogen is not prepared in the laboratory by the action of calcium with dilute sulphuric acid.
State why hydrogen is not prepared in the laboratory by the action of lead with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Give balanced equation for the following conversion:
Zinc to sodium zincate – using an alkali.
Give a balanced equation for the following conversions sodium plumbite from lead.
Give a balanced equation for the following conversions sodium aluminate from aluminium.
In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc and dil. acid. Give a reason for the following:
The complete apparatus is air-tight.
In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc and dil. acid. Give a reason for the following:
Dilute nitric acid is not preferred as the reactant acid.
In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc and dil. acid. Give a reason for the following:
The lower end of the thistle funnel should dip below the level of the acid in the flask.
In the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from zinc and dil. acid. Give a reason for the following:
Hydrogen is not collected over air.
‘Magnesium reacts with very dilute nitric acid at low temperatures liberating hydrogen.’ Give reasons.
State the condition and give balanced equation for the conversion of coke to water gas.
State the condition and give balanced equation for the conversion of water gas to hydrogen – in the Bosch process.
How are the unreacted gases separated out in ‘Bosch process’ in the manufacture of hydrogen.
Give a test to differentiate between two gas jars – one containing pure hydrogen and the other hydrogen-air mixture.
State the reactant added to hydrogen to obtain the respective product in following case.
Ammonia
State the reactant added to hydrogen to obtain the respective product in following case.
Hydrogen chloride
State the reactant added to hydrogen to obtain the respective product in following case.
Water
State the reactant added to hydrogen to obtain the respective product in following case.
Hydrogen sulphide
Discuss the use of hydrogen as a fuel ?
State the use of hydrogen –
In hydrogenation of oil and coal
State the use of hydrogen –
In the extraction of metals
Explain the term oxidation in term of addition and removal of oxygen/hydrogen with a suitable example.
Explain the term reduction in term of addition and removal of oxygen/hydrogen with a suitable example.
Explain the term redox reaction with an example involving the reaction of hydrogen sulphide with chlorine.
State what is oxidising agent. Give an example of oxidising agent in the gaseous, liquid, and solid form.
State what is reducing agent. Give an example of oxidising agent in the gaseous, liquid, and solid form.
Give two test for an oxidising agent.
Give two tests for a reducing agent.
Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 6 Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Hydrogen
Select the correct answer to the reactant added, to give the product in the preparation of hydrogen gas.
\[\ce{Ca(OH)2 + H2}\]
dilute acid
dilute alkali
cold water
conc. alkali
boiling water
conc. acid
steam
Select the correct answer to the reactant added, to give the product in the preparation of hydrogen gas.
\[\ce{MgO + H2}\]
dilute acid
dilute alkali
cold water
conc. alkali
boiling water
conc. acid
steam
Select the correct answer to the reactant added, to give the product in the preparation of hydrogen gas.
\[\ce{Fe3O4 + H2}\]
dilute acid
dilute alkali
cold water
conc. alkali
boiling water
conc. acid
steam
Select the correct answer to the reactant added, to give the product in the preparation of hydrogen gas.
\[\ce{Al2(SO4)3 + H2}\]
dilute acid
dilute alkali
cold water
conc. alkali
boiling water
conc. acid
steam
Select the correct answer to the reactant added, to give the product in the preparation of hydrogen gas.
\[\ce{NaAlO2 + H2}\]
dilute acid
dilute alkali
cold water
conc. alkali
boiling water
conc. acid
steam
Give a balanced equation for the following conversion.
\[\ce{MgCl2<-HCl->FeCl2}\]
Give a balanced equation for the following conversion.
\[\ce{KAlO2<-KOH->K2ZnO2}\]
Give a balanced equation for the following conversion.
\[\ce{ZnO<-H2O->Fe3O4}\]
Give a balanced equation for the following conversion.
\[\ce{CO + H2<-H2O->CO2 + H}\]
Give a balanced equation for the following conversion.
\[\ce{NH3<-H2->H2S}\]
Give a reason for the following.
Nitric acid in the dilute form is not used in the laboratory preparation of hydrogen from metals.
Give a reason for the following.
Granulated zinc is preferred to metallic zinc in the preparation of hydrogen using dilute acid.
Give a reason for the following.
Hydrogen and alkali metals of group 1 [IA] react with copper [II] oxide to give copper.
Give a reason for the following.
Hydrogen is collected by the downward displacement of water and not of air, even though it is lighter than air.
Give a reason for the following.
A mixture of hydrogen and chlorine can be separated by passage through a porous pot.
Name the following.
A metal below iron but above copper in the activity series of metals which has no reaction with water.
Name the following.
A metal which cannot be used for the preparation of hydrogen using dilute acids.
Name the following.
The salt formed when aluminium reacts with potassium hydroxide, during the preparation of hydrogen from alkalis.
Name the following.
A gaseous reducing agent which is basic in nature.
Name the following.
A compound formed between hydrogen and an element from group 17 [VIIA] – period 3.
Select the correct answer from the symbol in the bracket.
The element placed below hydrogen in group 1 [IA].
Na
Li
K
F
Select the correct answer from the symbol in the bracket.
The element other than hydrogen, which forms a molecule containing a single covalent bond.
Cl
N
O
Select the correct answer from the symbol in the bracket.
The element, which like hydrogen has one valence electron.
He
Na
F
O
Select the correct answer from the symbol in the bracket.
The element, which like hydrogen is a strong reducing agent.
Pb
Na
S
Cl
Select the correct answer from the symbol in the bracket.
The element which forms a diatomic molecule.
C
Br
S
P
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard
laboratory method.
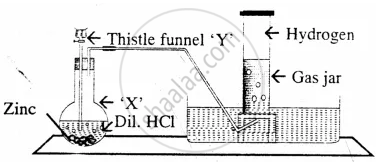
State what is added through the thistle funnel ‘Y’
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard laboratory method.

State what difference will be seen if pure zinc is added in the distillation flask ‘X’ instead of granulated zinc.
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard laboratory method.

Name a solution which absorbs the impurity – `"H"_2"S"`
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard laboratory method.

State, why hydrogen is collected after all the air in the apparatus, is allowed to escape.
The diagram represent the preparation and collection of hydrogen by a standard laboratory method.

Name a gas other than hydrogen collected by the same method.
Solutions for 6: Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen
![Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen - Shaalaa.com](/images/simplified-icse-chemistry-english-class-9_6:15cbe1f7c39e424a9ab3e108260ad612.jpg)
Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 6 - Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Viraf J. Dalal solutions for Mathematics Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 CISCE 6 (Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Viraf J. Dalal textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 chapter 6 Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen are Position of Hydrogen in Periodic Table, Similarities Between Hydrogen and Alkali Metals, Application of Activity Series in the Preparation of Hydrogen, Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen, Similarities Between Hydrogen and Halogens, Hydrogen, Preparation of Hydrogen, Manufacture of Hydrogen, Chemical Properties of Hydrogen, Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions, Uses of Hydrogen, Physical Properties of Hydrogen.
Using Viraf J. Dalal Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 solutions Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Viraf J. Dalal Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 students prefer Viraf J. Dalal Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Study Of The First Element — Hydrogen Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Simplified ICSE Chemistry [English] Class 9 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
