Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How are the less reactive metals (which are quite low in the reactivity series) extracted? Explain with the help of an example.
उत्तर
The ores of less reactive metals like copper and mercury are placed at the bottom of the reactivity series. Metals are extracted from these ores by heating them alone. We should note that ores of copper can be extracted by reduction with carbon (copper (I) oxide) as well as heating alone (copper (I) sulphide).
Let us explain this by taking the example of extraction of mercury from its cinnabar ore (HgS). Cinnabar is a sulphide ore. On heating the ore, mercury can be extracted. It is a sulphide ore; therefore, it is first heated in the presence of surplus air (roasting). This converts mercury (II) sulphide to mercury (II) oxide.

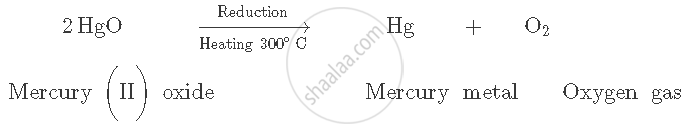
Mercury (II) oxide is then heated to around 300°C On heating, it gets reduced (decomposes) to mercury metal and oxygen gas is released.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The process by which sulphide ore is concentrated.
Give two uses of bronze.
What is the difference between a mineral and an ore?
The metal which can be extracted from the bauxite ore is:
(a) Na
(b) Mn
(c) Al
(d) Hg
The two metals which can be extracted just by heating their sulphides in air are:
(a) sodium and copper
(b) copper and aluminium
(c) potassium and zinc
(d) mercury and copper
Which of the following reactants are used to carry out the thermite reaction required for welding the broken railway tracks?
(a) Al2O3 + Fe
(b) MnO2 + Al
(c) Fe2O3 + Al
(d) Cu2O + Fe
How many valence electrons are present in metals ?
choose the most appropriate term to match the given description.
Heating of the ore in the absence of air to high temperature
Mercury, silver, gold are highly reactive metals.
Bauxite reacts with sodium hydroxide in the Bayer’s process.
