Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How are the less reactive metals (which are quite low in the reactivity series) extracted? Explain with the help of an example.
Solution
The ores of less reactive metals like copper and mercury are placed at the bottom of the reactivity series. Metals are extracted from these ores by heating them alone. We should note that ores of copper can be extracted by reduction with carbon (copper (I) oxide) as well as heating alone (copper (I) sulphide).
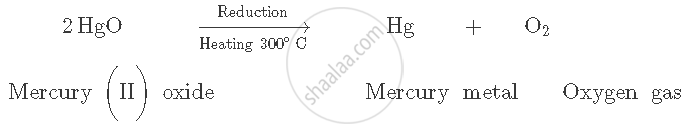
Let us explain this by taking the example of extraction of mercury from its cinnabar ore (HgS). Cinnabar is a sulphide ore. On heating the ore, mercury can be extracted. It is a sulphide ore; therefore, it is first heated in the presence of surplus air (roasting). This converts mercury (II) sulphide to mercury (II) oxide.

Mercury (II) oxide is then heated to around 300°C On heating, it gets reduced (decomposes) to mercury metal and oxygen gas is released.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name two metals which are always found in combined state.
What is the difference between a mineral and an ore?
An important ore of zinc metal is:
(a) calamine
(b) cuprite
(c) pyrolusite
(d) haematite
A sulphide ore is converted into metal oxide by the process of:
(a) carbonation
(b) roasting
(c) calcination
(d) anodising
Define the following term.
Mineral
Define roasting.
Bauxite reacts with sodium hydroxide in the Bayer’s process.
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Dry aluminium hydroxide is ignited at 1000 °C
An alloy is
Two ores A and B were taken. On heating ore A gives CO2 whereas, ore B gives SO2. What steps will you take to convert them into metals?
