Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals - Shaalaa.com](/images/9352831810-chemistry-science-english-class-10_6:7eeaf5db0f4a49c580d3c8746ff5ab36.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Metals and Non-metals
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CBSE Lakhmir Singh for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10.
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 3 Metals and Non-metals Exercise 1 [Pages 131 - 137]
Name one metal and one non-metal which exist in liquid state at room temperature.
Why are metals called electropositive elements whereas non-metals are called electronegative elements?
Name the most abundant metal in the earth's crust.
Name the most abundant non-metal in the earth's crust.
Name one metal which has a low melting point.
Name the metal which is the poorest conductor of heat.
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Non-metals react with dilute acids to produce a gas which burns with a 'pop' sound.
From amongst the metals sodium, calcium aluminium, copper and magnesium, name the metal:
(i) which reacts with water only on boiling, and
(ii) another which does not react even with steam.
What changes in the colour of iron nails and copper sulphate solution do you observe after keeping the iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution for about 30 minutes?
What is aqua-regia? Name two special metals which are insoluble in common reagents but dissolve in aqua-regia.
Give the name and formulae of two acidic oxides.
Give the name and formulae of two basic oxides.
What name is given to those metal oxides which show basic as well as acidic behaviour?
Name two metals which form amphoteric oxides.
A copper coin is kept immersed in a solution of silver nitrate for some time. What will happen to the coin and the colour of the solution?
Which property of copper and aluminium makes them suitable for making cooking utensils and boilers?
Which property of copper and aluminium makes them suitable for making electric wires?
Write the name and formulae of a metal hydride.
Write the name and formulae of a non-metal hydride.
Name the metal which has been placed at the bottom of the reactivity series.
Name the metal which has been placed at the top of the reactivity series.
Name the metal which has been placed just below copper in the reactivity series.
Which of the two metals is more reactive: copper or silver?
Name one metal which is stored in kerosene oil.
Name one non-metal which is stored under water.
Write equation for the reaction of sodium with oxygen.
Write equation for the reaction of magnesium with oxygen.
Name two metals which are used for making electric wires.
Name two metals which are used for making domestic utensils and factory equipment.
Name two metals which are used for making jewellery and to decorate sweets.
Which metal foil is used for packing some of the medicine tablets?
Name the non-metal which is used to convert vegetable oil into vegetable ghee (solid fat).
Name the non-metal which is used as a rocket fuel (in liquid form).
Name the non-metal which is used to make electrodes of dry cells.
Name the non-metal which is used to preserve food materials.
Name the non-metal which is used in the vulcanisation of rubber.
Name one property which is characteristic of metals.
Name one property which is characteristic of non-metals.
What is meant by "brittleness"? Which type of elements usually show brittleness: metals or non-metals?
What will happen if a strip of zinc is immersed in a solution of copper sulphate?
What will happen if a strip of copper is kept immersed in a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3)?
What changes in the colour of iron nails and copper sulphate solution do you observe after keeping the iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution for about 30 minutes?
How would you show that silver is chemically less reactive than copper?
Give reason for the following:
Blue colour of copper sulphate solution is destroyed when iron filings are added to it.
Name a non-metal having a very high melting point.
Which property of graphite is utilised in making electrodes?
Name two non-metals which are both brittle and non-ductile.
Explain why, the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Complete and balance the following equation:
Na + O2 →
Complete and balance the following equation:
Na2O + H2O →
Complete and balance the following equation:
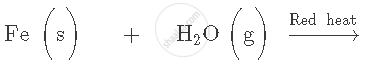
Complete and balance the following equation:
Cu (NO3)2 (aq) + Zn(s) →
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Magnesium liberates ............... gas on reacting with hot boiling water.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The white powder formed when magnesium ribbon burns in oxygen is of ....................
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Ordinary aluminium strips are not attacked by water because of the presence of a layer of ................. on the surface of aluminium.
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
A metal having low melting point is ..................... but a non-metal having very high melting point is ..............
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Calcium is a ................. reactive metal than sodium.
Explain the meaning of malleable.
Name two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Which property of iron metal is utilised in producing iron sheets required fro making buckets?
Which property of copper metal is utilised in making thin wires?
Name two metals which react violently with cold water. Write any three observations you would make when such a metal is dropped into water.
With the help of examples, describe how metal oxides differ from non-metal oxides.
Which of the following elements would yield an acidic oxide.
Na, S, C, K, H
Which of the following elements would yield a basic oxide.
Na, S, C, K, H
Which of the following elements would yield a neutral oxide?
Na, S, C, K, H
What are amphoteric oxides?
Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Choose the acidic oxides, basic oxides and neutral oxides from the following:
Na2O; CO2; CO; SO2; MgO; N2O; H2O.
Which of the following are amphoteric oxides:
MgO, ZnO, P2O3, Al2O3, NO2
What is the nature of the oxide SO2? What happens when it is dissolved in water? Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
What is the nature of the oxide Na2O? What happens when it is dissolved in water? Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
What type of oxides are formed when non-metals react with oxygen? Explain with an example.
What type of oxides are formed when metals combine with oxygen? Explain with the help of an example.
Explain why, metals usually do not liberate hydrogen gas with dilute nitric acid.
Name two metals which can, however, liberate hydrogen gas from very dilute nitric acid.
How do metals react with hydrogen? Explain with an example.
How do non-metals react with hydrogen? Explain with an example.
What happens when calcium reacts with chlorine? Write an equation for the reaction which takes place
What happens when magnesium reacts with very dilute nitric acid? Write an equation for the reaction involved.
Arrange the following metals in order of their chemical reactivity, placing the most reactive metal first:
Magnesium, Copper, Iron, Sodium, Zinc, Lead, Calcium.
What happens when a rod of zinc metal is dipped into a solution of copper sulphate? Give chemical equation of the reaction involved.
A copper plate was dipped in AgNO3 solution. After certain time, silver from the solution was deposited on the copper plate. State the reason why it happened. Give the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
State five uses of metals
State five uses of non-metals.
State one use of Copper.
State one use of Aluminium.
State one use of Iron.
State one use of Silver.
State one use of Gold.
State one use of Mercury.
State one use of Hydrogen.
State one use of Carbon (as Graphite).
State one use of Nitrogen.
State one use of Sulphur.
Name the metal which is used in making thermometers.
Why does aluminium not react with water under ordinary conditions?
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Name two metals which cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Why is white phosphorus kept immersed under water?
Can we keep sodium immersed under water? Why?
Describe the reaction of potassium with water. Write the equation of the reaction involved.
Write equations for the reactions of iron with steam.
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal?
Give one example, with equation, of the displacement of hydrogen by a metal from an acid.
Name two metals (other than zinc and iron) which can displace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid?
What is the action of water on sodium ? Write equation of the chemical reaction involved.
What is the action of water on magnesium ? Write equation of the chemical reaction involved.
What is the action of water on aluminium ? Write equation of the chemical reaction involved.
You are given samples of three metals − sodium, magnesium and copper. Suggest any two activities to arrange them in order of their decreasing reactivities.
Write one reaction in which aluminium oxide behaves as a basic oxide and another in which it behaves as an acidic oxide.
What special name is given to substances like aluminium oxide.
Name another metal oxide which behaves like aluminium oxide.
What happens when calcium reacts with water? Write the chemical equation of the reaction of calcium with eater.
Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place when iron reacts with dilute sulphuric acid. What happens when the gas produced is ignited with a burning matchstick?
You are given a dry cell, a torch bulb with holder, wires and crocodile clips. How would you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
State any five physical properties of metals.
State any five physical properties of non-metals.
Name two physical properties of sodium in which it's behaviour is not as expected from it's classification as metal.
Name two physical properties of carbon in which it's behaviour is not as expected from it's classification as non-metal.
Name two metals whose melting points are so low that they melt when held in the hand.
Metals are said to be shiny. Why do metals generally appear to be dull? How can their brightness be restored?
What are metals? Name five metals.
Name a metal which is so soft that it can be cut with a knife.
Name the metal which is the best conductor of heat and electricity.
What happens when a metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid? Explain with the help of an example.
Write the equation for the reaction of Magnesium with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Name the products formed. Also indicate the physical states of all the substances involved.
Write the equation for the reaction of Aluminium with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Name the products formed. Also indicate the physical states of all the substances involved.
Write the equation for the reaction of Zinc with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Name the products formed. Also indicate the physical states of all the substances involved.
Write the equation for the reaction of Iron with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Name the products formed. Also indicate the physical states of all the substances involved.
Define non-metals. Give five examples of non-metals.
Name a non-metal which conducts electricity.
Name a non-metal having lustre (shining surface).
Name a non-metal which is extremely hard.
How do non-metals react with oxygen? Explain with an example. Give equation of the reaction involved. What is the nature of the product formed? How will you demonstrate it?
What is meant by the reactivity series of metals? Arrange the following metals in an increasing order of their reactivities towards water:
Zinc, Iron, Magnesium, Sodium
Hydrogen is not a metal but still it has been assigned a place in the reactivity series of metals. Why?
Name one metal more reactive and another less reactive than hydrogen.
Name one metal which displaces copper from copper sulphate solution and one which does not.
Name one metal which displaces silver from silver nitrate solution and one which does not.
State any three differences between the physical properties of metals and non-metals.
Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
State three reasons (of which at least one must be chemical) for believing that sodium is a metal.
State three reasons (of which at least one must be chemical) for believing that sulphur is a non-metal.
Which non-metal has been placed in the reactivity series of metals?
The elements whose oxides can turn phenolphthalein solution pink are:
(a) Na and K
(b) K and C
(c) Na and S
(d) K and P
"Is malleable and ductile". This best describes:
(a) a metal
(b) a compound
(c) a non-metal
(d) a solution
One of the following is not a neutral oxide. This is:
(a) CO
(b) H2O
(c) N2O
(d) Na2O
A basic oxide will be formed by the element:
(a) K
(b) S
(c) P
(d) Kr
An acidic oxide is produced by the element:
(a) Na
(b) C
(c) Ca
(d) H
You are given a solution of AgNO3. Which of the following do you think cannot displace Ag from AgNO3solution?
(a) Magnesium
(b) Zinc
(c) Gold
(d) Copper
Out of aluminium, copper, calcium and tin, the most reactive metal is:
(a) aluminium
(b) copper
(c) tin
(d) calcium
The least reactive metal among the following is:
(a) sodium
(b) silver
(c) copper
(d) lead
An element X reacts with hydrogen, when heated, to form a covalent hydride H2X. If H2X has a smell of rotten eggs, the element X is likely to be:
(a) carbon
(b) sulphur
(c) chlorine
(d) phosphorus
Out of the following oxides, the amphoteric oxide is:
(a) Fe2O3
(b) Al2O3
(c) P2O5
(d) N2O
The metals which can produce amphoteric oxides are:
(a) sodium and aluminium
(b) zinc and potassium
(c) calcium and sodium
(d) aluminium and zinc
An element X forms two oxides XO and XO2. The oxide XO is neutral but XO2 is acidic in nature. The element X is most likely to be:
(a) sulphur
(b) carbon
(c) calcium
(d) hydrogen
The elements whose oxides can turn litmus solution blue are:
(a) carbon and sulphur
(b) sodium and carbon
(c) potassium and magnesium
(d) magnesium and sulphur
The elements whose oxides can turn litmus solution red are:
(a) lithium and sodium
(b) copper and potassium
(c) carbon and hydrogen
(d) phosphorus and sulphur
Zinc oxide is a metal oxide. Which of the following term best describes the nature of zinc oxide:
(a) an acidic oxide
(b) a basic oxide
(c) an amphoteric oxide
(d) a neutral oxide
A metal less reactive and another metal more reactive than hydrogen are:
(a) aluminium and lead
(b) iron and magnesium
(c) copper and tin
(d) copper and mercury
An element E reacts with water to form a solution which turns phenolphthalein solution pink. The element E is most likely to be:
(a) S
(b) Ca
(c) C
(d) Ag
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be:
calcium
carbon
silicon
iron
Which one of the following four metals would be displaced from the solution of its salt by the other three metals?
(a) Zn
(b) Ag
(c) Cu
(d) Mg
An element is soft and can be cut with a knife. If is very reactive and cannot be kept open in the air. It reacts vigorously with water. The element is most likely to be:
(a) Mg
(b) S
(c) P
(d) Na
Which of the following metal exists in the liquid state?
(a) Na
(b) Ag
(c) Cr
(d) Hg
Which of the following non-metal is a liquid?
(a) carbon
(b) sulphur
(c) bromine
(d) iodine
Which of the following pair of reactants can undergo a displacement reaction under appropriate conditions?
(a) MgSO4 + Fe
(b) ZnSO4 + Fe
(c) MgSO4 + Pb
(d) CuSO4 + Fe
An element E forms an oxide E2O. An aqueous solution of E2O turns red litmus paper blue.
(a) What is the nature of the oxide E2O?
(b) State whether element E is a metal or a non-metal.
(c) Give one example of an element like E.
Metal A burns in air, on heating, to form an oxide A2O3 whereas another metal B burns in air only on strong heating to form an oxide BO. The two oxides A2O3 and BO can react with hydrochloric acid as well as sodium hydroxide solution to form the corresponding salts and water.
(a) What is the nature of oxide A2O3?
(b) What is the nature of oxide BO?
(c) Name one metal like A.
(b) Name one metal like B.
An element X forms two oxides XO and XO2. The oxide XO has no action on litmus solution but oxide XO2 turns litmus solution red.
(a) What is the nature of oxide XO?
(b) What is the nature of oxide XO2?
(c) Would you call element X a metal or a non-metal? Give reason for your choice.
(d) Can you give an example of element like X?
State and explain the reaction, if any, of the following metals with a solution of copper sulphate:
(a) Gold
(b) Copper
(c) Zinc
(d) Mercury
(a) Give the names and formulae of one metal chloride and one non-metal chloride.
(b) State an important property in which these metal chloride and non-metal chloride differ.
(c) Why do they differ in this property?
In a solution of lead acetate, a strip of metal M was dipped. After some time, lead from the solution was deposited on the metal strip. Which metal is more reactive, M or lead?
CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
FeSO4(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
On the basis of the above reactions, indicate which is most reactive and which is least reactive metal out of zinc, copper and iron.
Which of the following reactions will not occur? Why not?
(a) MgSO4 (aq) + Cu (s) → CuSO4 (aq) + Mg (s)
(b) CuSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(c) MgSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) → FeSO4 (aq) + Mg (s)
In nature, metal A is found in a free state while metal B is found in the form of its compounds. Which of these two will be nearer to the top of the activity series of metals?
If A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J and K represent metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity, which one of them is most likely to occur in a free state in nature?
Name a metal which does not react with cold as well as hot water but reacts with steam.
Name a metal which It does not react with any physical state of water?
When calcium metal is added to water, the gas evolved does not catch fire but the same gas evolved on adding sodium metal to water catches fire. Why is it so?
A zinc plate was kept in a glass container having CuSO4 solution. On examining it was found that the blue colour of the solution is getting lighter and lighter. After a few days, when the zinc plate was taken out of the solution, a number of small holes were noticed in it. State the reason and give chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 3 Metals and Non-metals Exercise 2 [Pages 167 - 172]
What is the name of the chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two atoms?
What is the name of the chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another?
Name a carbon containing molecule which has two double bonds.
What would be the electron-dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
What type of chemical bond is formed between potassium and bromine?
What type of chemical bond is formed between carbon and bromine?
What do we call those particles which have more or less electrons than the normal atoms?
What do we call those particles which have more electrons than the normal atoms?
What do we call those particles which have less electrons than the normal atoms?
The atomic number of sodium is 11. What is the number of electrons in Na+?
The atomic number of chlorine is 17. What is the number of electrons in Cl−?
The atomic number of an element X is 8 and that of element Y is 12. Write down the symbols of the ions you would expect to be formed from their atoms.
Write down the electronic configuration of magnesium atom.
(At. No. of Mg = 12)
Write down the electronic configuration of magnesium ion.
(At. No. of Mg = 12)
Write down the electronic configuration of sulphur atom.
(At. No. of S = 16)
Write down the electronic configuration of sulphide ion.
(At. No. of S = 16)
What type of chemical bonds are present in a solid compound which has a high melting point, does not conduct electricity in the solid state but becomes a good conductor in the molten state?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
The aqueous solution of an ionic compound conducts electricity because there are plenty of free electrons in the solution.
What type of bonds are present in hydrogen chloride and oxygen?
Write the electron-dot structure for the following molecule?
NaCl
Write the electron-dot structure for the following molecule.
Cl2
What type of bonds are present in water molecule? Draw the electron-dot structure of water (H2O).
What type of bonds are present in methane (CH4) and sodium chloride (NaCl)?
State one major difference between covalent and ionic bonds and give one example each of covalent and ionic compounds.
What type of bonds are present in H2 molecule? Draw their electron-dot structures.
What type of bonds are present in CH4 molecule? Draw their electron-dot structures.
What type of bonds are present in Cl2 molecule? Draw their electron-dot structures.
What type of bonds are present in CO2 molecule? Draw their electron-dot structures.
Which inert gas electron configuration do the Cl atoms in Cl2 molecule resemble? What is this electron configuration?
Which of the following compounds are ionic and which are covalent?
Urea, Cane sugar, Hydrogen chloride, Sodium chloride, Ammonium chloride, Carbon tetrachloride, Ammonia, Alcohol, Magnesium chloride.
Give one example of a molecule containing a single covalent bond.
Give one example of a molecule containing a double covalent bond
Give one example of a molecule containing a triple covalent bond.
Give one example of a molecule containing a ionic covalent bond.
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
Two atoms of the same element combine to form a molecule. The bond between them is known as ................ bond.
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
Two chlorine atoms combine to form a molecule. The bond between them is known as ..........
Fill in the blanks in the following sentence:
In forming oxygen molecule, .............. electrons are shared by each atom of oxygen.
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
In forming N2 molecule, .............. electrons are shared by each atom of nitrogen.
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
The number of single covalent bonds in C2H2 molecule are ...........
What is a covalent bond?
What type of bond exist in CCl4?
What type of bond exist in Cacl2?
What is an ionic bond?
What type of bond is present in oxygen molecule?
What is an ion? Explain with examples?
What is the nature of charge on a cation?
What is the nature of charge on an anion?
Name the cation and anion present in MgCl2. Also write their symbols.
What type of chemical bond is present in chlorine molecule? Explain your answer.
Explain the formation of a chlorine molecule on the basis of electronic theory of valency.
Give one example , state what are ionic compounds?
Give one example, state what are covalent compounds?
Compare the properties of ionic compounds and covalent compounds.
Explain why covalent compounds have generally high melting points?
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Give two general properties of ionic compounds and two those of covalent compounds.
State one test by which sodium chloride can be distinguished from sugar.
Explain why, ionic compounds conduct electricity in solution whereas covalent compounds do not conduct electricity.
will MgCl2 conduct electricity or not?
give reason for your choice.
will CCl4 conduct electricity or not?
give reason for your choice.
will NaCl conduct electricity or not?
give reason for your choice.
will CS2 conduct electricity or not?
give reason for your choice.
will Na2S conduct electricity or not?
give reason for your choice.
Name one ionic compound containing chlorine.
Name one covalent compound containing chlorine.
How will you find out which of the water soluble compound A or B is ionic?
Explain why, a solution of cane sugar does not conduct electricity but a solution of common salt is a good conductor of electricity.
Give the formula of the compound that would be formed by the combination of the following pair of elements:
Mg and N2
Give the formula of the compound that would be formed by the combination of the following pair of elements:
Li and O2
Give the formula of the compound that would be formed by the combination of the following pair of elements:
Al and Cl2
Give the formula of the compound that would be formed by the combination of the following pair of elements:
K and H
What are noble gases
What is the characteristic of the electronic configuration of noble gases?
What is the cause of chemical bonding (or chemical combination) of atoms of elements?
Write electron-dot structures for magnesium and oxygen.
Show the formation of MgO by the transfer of electrons.
What are the ions present in this compound?
Draw the electron-dot structure of a hydrogen chloride molecule.
Which inert gas does the H atom in HCl resemble in electron arrangement?
Which inert gas does the Cl atom in HCl resemble in electron arrangement?
What type of bonding would you expect between Calcium and Oxygen?
What type of bonding would you expect between Carbon and Chlorine?
What type of bonding would you expect between Hydrogen and Chlorine?
Describe how sodium and chlorine atoms are changed into ions when they react with each other to form sodium chloride, NaCl. What is the name given to this type of bonding? (At. No of sodium = 11; At. No. of chlorine = 17)
What is the difference between a cation and an anion? How are they formed? Give the names and symbols of one cation and one anion.
Using electron-dot diagrams which show only the outermost shell electrons, show how a molecule of nitrogen, N2, is formed from two nitrogen atoms. What name is given to this type of bonding? (Atomic number of nitrogen is 7)
Draw the electron-dot structure of CO2 compound and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of MgO compound and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of H2O compound and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of HCl compound and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of MgCl2 compound and state the type of bonding.
Using electron-dot diagrams which show only the outermost shell electrons, show how a molecule of oxygen, O2, is formed from two oxygen atoms. What name is given to this type of bonding? (At. No. of oxygen = 8)
Draw the electron-dot structure of KCl and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of NH3 and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of CaO and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of N2 and state the type of bonding.
Draw the electron-dot structure of CaCl2 and state the type of bonding.
Explain why, a salt which does not conduct electricity in the solid state becomes a good conductor in molten state.
Write down the electronic configuration of sodium atom.
Write down the electronic configuration of chlorine atom.
How many electrons are there in the outermost shell of a sodium atom.
How many electrons are there in the outermost shell of a chlorine atom?
Show the formation of NaCl from sodium and chlorine atoms by the transfer of electron(s).
Why has sodium chloride a high melting point?
Name the anode and the cathode used in the electrolytic refining of impure copper metal.
Write the electron arrangement in a magnesium atom.
Write the electron arrangement in an oxygen atom.
How many electrons are there in the valence shell of a magnesium atom?
How many electrons are there in the valence shell of an oxygen atom?
Show on a diagram the transfer of electrons between the atoms in the formation of MgO.
Name the solvent in which ionic compounds are generally soluble.
Why are aqueous solution of ionic compounds able to conduct electricity?
What is the electronic configuration of a sodium atom?
What is the electronic configuration of an oxygen atom?
What is the number of outermost electrons in a sodium atom?
What is the number of outermost electrons in an oxygen atom?
Show the formation of Na2O by the transfer of electrons between the combining atoms.
Why are ionic compounds usually hard ?
How is it that ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity but they do so when in molten state?
Write the electron arrangement in a magnesium atom.
Write down the electron arrangement in a chlorine atom.
How many electrons are there in the valence shell of a magnesium atom?
How many electrons are there in the valence shell of a chlorine atom?
Show the formation of magnesium chloride from magnesium and chlorine by the transfer of electrons.
State whether magnesium chloride will conduct electricity or not. Give reason for your answer.
Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity?
The atomic number of an element X is 19. The number of electrons in its ion X+ will be:
(a) 18
(b) 19
(c) 20
(d) 21
The atomic number of an element Y is 17. The number of electrons in its ion Y− will be:
(a) 17
(b) 18
(c) 19
(d) 20
The atomic numbers of four elements A, B, C and D are 6, 8, 10 and 12 respectively. The two elements which can react to form ionic bonds (or ionic compound) are:
(a) A and D
(b) B and C
(c) A and C
(d) B and C
The atomic numbers of four elements P, Q, R and S are 6, 10, 12 and 17 respectively. Which two elements can combine to form a covalent compound?
(a) P and R
(b) Q and S
(c) P and S
(d) R and S
The solution of one of the following compounds will not conduct electricity. This compounds is:
(a) NaCl
(b) CCl4
(c) MgCl2
(d) CaCl2
The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are:
| X : 2 | Y : 2, 8, 7 | Z : 2, 8, 2 |
Which of the following is correct regarding these elements?
(a) X is a metal
(b) Y is a metal
(c) Z is a non-metal
(d) Y is a non-metal and Z is a metal
Which one of the following property is generally not exhibited by ionic compounds?
(a) solubility in water
(b) electrical conductivity in solid state
(c) high melting and boiling points
(d) electrical conductivity in molten state
The electrons present in the valence shell of a noble gas atom can be:
(a) 8 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 8 or 2
(d) 8 or 4
The atomic number of an element X is 16. The symbol of ion formed by an atom of this element will be:
(a) X2+
(b) X3+
(c) X2−
(d) X−
The number of protons in the nucleus of one atom of an element Y is 5. The symbol of ion formed by an atom of this element will be:
(a) Y3−
(b) Y2+
(c) Y2−
(d) Y3+
Out of KCl, HCl, CCl4 and NaCl, the compounds which are not ionic are:
(a) KCl and HCl
(b) HCl and CCl4
(c) CCl4 and NaCl
(d) KCl and CCl4
Element X reacts with element Y to form a compound Z. During the formation of compound Z, atoms of X lose one electron each whereas atoms of Y gain one electron each. Which of the following property is not shown by compound Z?
(a) high melting point
(b) low melting point
(c) occurrence as solid
(d) conduction of electricity in molten state
One of the following compounds is not ionic in nature. This compound is:
(a) Lithium chloride
(b) Ammonium chloride
(c) Calcium chloride
(d) Carbon tetrachloride
The rechargeable battery used in a mobile phone hand set is usually:
(a) lead ion battery
(b) sodium ion battery
(c) hydrogen ion battery
(d) lithium ion battery
The number of protons in one atom of an element X is 8. What will be the number of electrons in its ion X2−?
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 10
(d) 11
If the number of protons in one atom of an element Y is 20, then the number of electrons in its ion Y2+will be:
(a) 20
(b) 19
(c) 18
(d) 16
The noble gas having only two electrons in its valence shell is:
(a) Ar
(b) Ne
(c) He
(d) Kr
A covalent molecule having a double bond between its atoms is:
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Oxygen
(c) water
(d) ammonia
The molecules having triple bond in them are:
(a) oxygen and ethyne
(b) carbon dioxide and ammonia
(c) methane and ethene
(d) nitrogen and ethyne
One of the following contains a double bond as well as single bonds. This is:
(a) CO2
(b) O2
(c) C2H4
(d) C2H2
Which of the following has a triple bond as well as single bonds?
(a) ethene
(b) methane
(c) ethyne
(d) nitrogen
Two non-metals combine with each other by the sharing of electrons to form a compound X.
(a) What type of chemical bond is present in X?
(b) State whether X will have a high melting point or low melting point.
(c) Will it be a good conductor of electricity or not?
(d) Will it dissolve in an organic solvent or not?
A metal combines with a non-metal by the transfer of electrons to form a compound Y.
(i) State the type of bonds in Y.
(ii) What can you say about its melting point and boiling point?
(iii) Will it be a good conductor of electricity?
(iv) Will it dissolve in an organic solvent or not?
The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are as follows:
| X | 2, 4 |
| Y | 2, 7 |
| Z | 2, 1 |
(a) Which two elements will combine to form an ionic compound?
(b) Which two elements will react to form a covalent compound?
Give reasons for your choice.
An element A has 4 valence electrons in its atom whereas element B has only one valence electron in its atom. The compound formed by A and B does not conduct electricity. What is the nature of chemical bond in the compound formed? Give its electron-dot structure.
In the formation of a compound XY2 atom X gives one electron to each Y atom. What is the nature of bond in XY2? Give two properties of XY2.
An element 'A' has two electrons in the outermost shell of its atom and combines with an element 'B' having seven electrons in the outermost shell, forming the compound AB2. The compound when dissolved in water conducts electric current. Giving reasons, state the nature of chemical bond in the compound.
The electronic configurations of two elements A and B are given below:
| A | 2, 6 |
| B | 2, 8, 1 |
(a) What type of chemical bond is formed between the two atoms of A?
(b) What type of chemical bond will be formed between the atoms of A and B?
Four elements A, B, C and D have the following electron arrangements in their atoms:
| A | 2, 8, 6 |
| B | 2, 8, 8 |
| C | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
| D | 2, 7 |
(a) What type of bond is formed when element C combines with element D?
(b) Which element is an inert gas?
(c) What will be the formula of the compound between A and C?
An element X of atomic number 12 combines with an element Y of atomic number 17 to form a compound XY2. State the nature of chemical bond in XY2 and show how the electron configurations of X and Y change in the formation of this compound.
The electronic configurations of three elements A, B and C are as follows:
| A | 2, 8, 1 |
| B | 2, 8, 7 |
| C | 2, 4 |
(a) Which of these element is a metal?
(b) Which of these elements are non-metals?
(c) Which two elements will combine to form an ionic bond?
(d) Which two elements will combine to form a covalent bond?
(e) Which element will form an anion of valency 1?
The electronic configurations of four particles A, B, C and D given below:
| A | 2, 8, 8 |
| B | 2, 8, 2 |
| C | 2, 6 |
| D | 2, 8 |
Which electronic configuration represents:
(i) magnesium atom?
(ii) oxygen atom?
(iii) sodium ion
(iv) chloride ion?
The atomic number of an element X is 12.
(a) What must an atom of X do to attain the nearest inert gas electron configuration?
(b) Which inert gas is nearest to X?
The atomic number of an element Y is 16.
(a) What must an atom of Y do to achieve the nearest inert gas electron arrangement?
(b) Which inert gas is nearest to Y?
You can buy solid air-freshners in shops. Do you think these substance are ionic or covalent? Why?
Give the formulae of the chlorides of the elements X and Y having atomic numbers of 3 and 6 respectively. Will the properties of the two chlorides be similar or different? Explain your answer.
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 3 Metals and Non-metals Exercise 3 [Pages 191 - 196]
A zinc ore gave CO2 on treatment with a dilute acid. Identify the ore and write its chemical formula.
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Write two methods of preventing the rusting of iron.
What is meant by galvanisation? Why is it done?
Name the metal which is used for galvanising iron.
Explain why, iron sheets are coated with zinc.
Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Give reasons.
Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Name a reducing agent that may be used to obtain manganese from manganese dioxide.
Name an alloy of lead and tin.
Give the composition of an alloy called solder. State its one property and one use.
What is an amalgam?
How many carats is pure gold? Why is pure gold not suitable for making ornaments?
Name one method for the refining of metals.
State two conditions for the rusting of iron.
In one method of rust prevention, the iron is not coated with anything. Which is this method?
Name two alloys of iron. What elements are present in these alloys?
Give reasons:
Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
Which metal becomes black in the presence of hydrogen sulphide gas in air?
Name the gas in air which tarnishes silver articles slowly.
Silver metal does not combine easily with oxygen but silver jewellery tarnishes after some time. How?
Write the composition of the alloy called bronze.
Give two uses of bronze.
Why does a new aluminium vessel lose shine so soon after use?
Why do gold ornaments look new even after several years of use?
Name two metals which are highly resistant to corrosion.
Which property of 'solder' alloy makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Explain why, carbon cannot reduce oxides of sodium or magnesium.
Why are the metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg never found in their free state in nature?
Name one metal which is extracted by reduction with carbon.
Name one metal which is extracted by electrolytic reduction.
Name one metal which is extracted by reduction with aluminium.
Name one metal which is extracted by reduction with heat alone.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The corrosion of iron is called ................
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
............ and .............. are necessary for the rusting of iron.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The process of depositing a thin layer of zinc on iron articles is called .............
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words:
Tiffin boxes are electroplated with .............. but car bumpers are electroplated with ............... to protect them from rusting.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The corrosion of copper produces a .............. coating of basic copper carbonate on its surface
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Brass is an alloy of copper and .........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Bronze is an alloy of copper and .........
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The non-metal present in steel is ............
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The alloy in which one of the metals is mercury is called an ...............
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The electrical conductivity and melting point of an alloy is ........... than that of pure metals.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The rocky material found with ores is called.............
How is manganese extracted from manganese dioxide, MnO2? Explain with the help of an equation.
What is a thermite reaction? Explain with the help of an equation. State one use of this reaction.
Which one of the methods given in column I is applied for the extraction of each of the metals given in column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| Electrolytic reduction | Aluminium |
| Reduction with Carbon | Zinc |
| Reduction with Aluminium | Sodium |
| Iron | |
| Manganese | |
| Tin |
Give reasons why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron).
Explain why, the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Why does aluminium not corrode right through?
What is anodising? Give its applications.
Why is an iron grill painted frequently?
Explain why, through aluminium is more reactive than iron, yet there is less corrosion of aluminium when both are exposed to air.
Name the method by which aluminium metal is extracted.
Give the name and chemical formula of one ore of copper.
How is zinc extracted from its carbonate or (calamine)? Explain with equations.
Name two metals which occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
Name one ore of manganese. Which compound of manganese is present in this ore? Also write its chemical formula.
A zinc ore on heating in air forms sulphur dioxide. Describe briefly any two stages involved in the conversion of this concentrated ore into zinc metal.
Explain giving one example, how highly reactive metals (which are high up in the reactivity series) are extracted.
Describe with one example, how moderately reactive metals (which are in the middle of reactivity series) are extracted.
How are the less reactive metals (which are quite low in the reactivity series) extracted? Explain with the help of an example.
What is meant by refining of a metal? Name the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals obtained by various reduction processes. Describe this method with the help of a labelled diagram by taking the example of any metal.
Define the term mineral.
Define the term ore.
What is meant by the 'concentration of ore'?
Define the terms gangue.
Name one ore of copper (other than cuprite). Which compound of copper is present in this ore? Also, write its chemical formula.
Explain how, a reduction reaction of aluminium can be used for welding cracked machine parts of iron. Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
What is corrosion?
Name any two metals which do not corrode easily.
What is the corrosion of iron known as?
Give reasons.
Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
What is meant by 'rusting of iron'? With the help of labelled diagrams, describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
What is an alloy? How is an alloy made?
What elements are present in steel? How are the properties of steel different from those of pure iron?
Give the constituents and one use of brass.
Name two metals which resist corrosion due to the formation of a thin, hard and impervious layer of oxide on their surface.
Name five methods of preventing rusting of iron.
What are the constituents of stainless steel?
What are the special properties of stainless steel?
Name an alloy of copper. State its chemical composition and any one use.
Explain why, when a copper object remains in damp air for a considerable time, a green coating is formed on its surface. What is this process known as?
How does the electrical conductivity of copper alloys, brass and bronze, differ from that of pure copper?
What is meant by 22 carat gold? Name the metals which are usually alloyed with gold to make it harder.
Explain given equation, what happens when ZnCO3 is heated in the absence of air?
Explain givem equation, what happens when a mixture of Cu2O and Cu2S is heated?
For the reduction of metal oxide, suggest a reducing agent other than carbon.
Explain why, an aqueous solution of sodium chloride is not used for the electrolytic extraction of sodium metal.
How are metals refined by the electrolytic process? Describe the electrolytic refining of copper with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
Name the chemical compound which is electrolysed in molten state to obtain aluminium metal. Which gas is evolved during this process?
Name the chemical compound which is electrolysed in molten state to obtain sodium metal. Which gas is produced in this process?
Name the gas produced when calamine ore is calcined.
Name the gas evolved when cinnabar ore is roasted.
Name two metals which are found in nature mainly in the free state (as metallic elements).
Name two metals which are always found in combined state.
What iron compound is present in haematite ore? Also write its chemical formula.
What is the difference between a mineral and an ore?
Which metal is extracted from cinnabar ore?
Name one ore of sodium. Name the sodium compound present in this ore and write its chemical formula.
How is sodium metal extracted? Explain with the help of equation of the reaction involved.
Name three other metals which are extracted in a manner similar to sodium.
Name the metal which is extracted from haematite ore.
Name one ore of aluminium. Name the aluminium compound present in this ore and write its chemical formula.
How is aluminium metal extracted? Explain with the help of an equation.
Name the electrode at which aluminium metal is produced.
Which gas is produced during the extraction of aluminium? At which electrode is this gas produced?
Which metal is extracted from bauxite ore?
Give the name of one ore of iron. Which iron compound is present in this ore? Write its chemical formula.
Describe the extraction of zinc metal from its sulphide ore (zinc blende). Write equations of the reactions involved.
Explain why, the galvanised iron article is protected against rusting even if the zinc layer is broken.
Name a common metal which is highly resistant to corrosion.
Name the metal which is extracted from the ore called 'rock salt'.
Name two ores of zinc. Write the names of the chemical compounds present in them and give their chemical formulae.
Explain how, mercury is extracted from its sulphide ore (cinnabar). Give equations of the reactions involved.
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Name any five metals which are purified by electrolytic refining method.
Which metal is extracted from calamine ore?
Name one ore of mercury. Which mercury compound is present in this ore? Write its chemical formula.
How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore (copper glance), Cu2S? Explain with equations of the reactions involved.
What is an alloy? Give two examples of alloys.
How are the properties of an alloy different from those of the constitutent elements?
An ore of manganese metal is:
(a) bauxite
(b) haematite
(c) cuprite
(d) pyrolusite
Which of the following is an iron ore?
(a) cinnabar
(b) calamine
(c) haematite
(d) rock salt
The metal which can be extracted from the bauxite ore is:
(a) Na
(b) Mn
(c) Al
(d) Hg
The two metals which can be extracted just by heating their sulphides in air are:
(a) sodium and copper
(b) copper and aluminium
(c) potassium and zinc
(d) mercury and copper
A common metal which is highly resistant to corrosion is:
(a) iron
(b) copper
(c) aluminium
(d) magnesium
An important ore of zinc metal is:
(a) calamine
(b) cuprite
(c) pyrolusite
(d) haematite
The major ore of aluminium is known as:
(a) cinnabar
(b) calamine
(c) bauxite
(d) pyrolusite
The two metals which are extracted by means of electrolytic reduction of their molten salts are:
(a) magnesium and manganese
(b) iron and aluminium
(c) zinc and magnesium
(d) magnesium and aluminium
In stainless steel alloy, iron metal is mixed with:
(a) Cu and Cr
(b) Cr and Ni
(c) Cr and Sn
(d) Cu and Ni
If copper is kept exposed to damp air for a considerable time, it gets a green coating on its surface. This is due to the formation of:
(a) hydrated copper sulphate
(b) copper oxide
(c) basic copper carbonate
(d) copper nitrate
Which of the following alloys contains mercury as one of the constituents?
(a) stainless steel
(b) solder
(c) duralumin
(d) zinc amalgam
Which of the following is an ore of mercury metal?
(a) rock salt
(b) cinnabar
(c) calamine
(d) haematite
Calamine ore can be used to extract one of the following metals. This metal is:
(a) copper
(b) mercury
(c) aluminium
(d) zinc
Which of the following pair of metals exists in their native state in nature?
(a) Ag and Hg
(b) Ag and Zn
(c) Au and Hg
(d) Au and Ag
Which of the following reactants are used to carry out the thermite reaction required for welding the broken railway tracks?
(a) Al2O3 + Fe
(b) MnO2 + Al
(c) Fe2O3 + Al
(d) Cu2O + Fe
Which of the following alloys contains a non-metal as one of the constituents?
(a) brass
(b) amalgam
(c) steel
(d) bronze
During the refining of an impure metal by electrolysis, the pure metal is a deposited:
(a) at cathode
(b) on the walls of electrolytic tank
(c) at anode
(d) at the bottom of electrolytic tank
Which of the following metals can be obtained from haematite ore?
(a) copper
(b) sodium
(c) zinc
(d) iron
Brass is an alloy of:
(a) Cu and Sn
(b) Cu and Pb
(c) Pb and Sn
(d) Zn and Cu
The metal which is always present in an amalgam is:
(a) iron
(b) aluminium
(c) mercury
(d) magnesium
Manganese metal is extracted from manganese dioxide by a reduction process by making use of:
(a) carbon
(b) hydrogen
(c) electrolysis
(d) aluminium
The metal which can be extracted simply by heating the cinnabar ore in air is:
(a) Zn
(b) Cu
(c) Al
(d) Hg
During galvanisation, iron metal is given a thin coating of one of the following metals. This metal is:
(a) chromium
(b) tin
(c) zinc
(d) copper
Which of the following metals are extracted by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides?
(a) Na and Hg
(b) Hg and Mg
(c) Na and Mg
(d) Cu and Fe
Rock salt is an ore of one of the following metals. This metal is:
(a) Mn
(b) Na
(c) Fe
(d) Cu
The articles made of silver metal become dark on prolonged exposure to air. This is due to the formation of a layer of its:
(a) oxide
(b) hydride
(c) sulphide
(d) carbonate
A sulphide ore is converted into metal oxide by the process of:
(a) carbonation
(b) roasting
(c) calcination
(d) anodising
The metal which can be extracted from pyrolusite ore is:
(a) mercury
(b) manganese
(c) aluminium
(d) magnesium
Calamine ore can be converted into zinc oxide by the process of:
(a) dehydration
(b) roasting
(c) calcination
(d) sulphonation
Zinc blende ore can be converted into zinc oxide by the process of:
(a) roasting
(b) hydrogenation
(c) chlorination
(d) calcination
An element A which is a part of common salt and kept under kerosene reacts with another element B of atomic number 17 to give a product C. When an aqueous solution of product C is electrolysed then a compound D is formed and two gases are liberated.
(a) What are A and B?
(b) Identify C and D.
(c) What will be the action of C on litmus solution? Why?
(d) Write formula of the compound formed when element B reacts with an element E having atomic number 5.
A metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide ore in the presence of air.
(a) Name the metal and write its chemical symbol.
(b) Write the name and formula of the sulphide ore.
(c) Give the equations of chemical reactions involved in the production of metal from its sulphide ore.
(d) Name a common device in which this metal is used.
(e) Can this metal displace copper from copper sulphate solution? Why?
No chemical reaction takes place when granules of a rusty-brown solid A are mixed with the powder of another solid B. However, when the mixture is heated, a reaction takes place between its components. One of the products C is a metal and settles down in the molten state while the other product D floats over it. It was observed that the reaction is highly exothermic.
(a) What could the solids A and B be?
(b) What are the products C and D most likely to be?
(c) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between A and B leading to the formation of C and D. Mention the physical states of all the reactants and products in this equation and indicate the heat change which takes place.
(d) What is the special name of such a reaction? State one use of such a reaction.
(e) Name any two types of chemical reactions under which the above reaction can be classified.
In an electrolytic tank, aluminium metal is being extracted by the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide using carbon electrodes. It is observed that one of the carbon electrodes is gradually burnt away and has to be replaced.
(a) Which carbon electrode (cathode or anode) is burnt away?
(b) Why is this carbon electrode burnt away?
A metal X which is resistant to corrosion is produced by the electrolysis of its molten oxide whereas another metal Y which is also resistant to corrosion is produced by the reduction of its oxide with carbon. Metal X can be used in powder form in thermite welding whereas metal Y is used in making cathodes of ordinary dry cells.
(a) Name the metals X and Y.
(b) Which of the two metals is more reactive : X or Y?
(c) Name one ore or metal X. Also write its chemical formula.
(d) Name one ore or metal Y. Also write its chemical formula.
(e) Name one alloy of metal X and one alloy of metal Y.
When an object made of metal A is kept in air for a considerable time, it loses its shine and becomes almost black due to the formation of a layer of substance B. When an object made of another metal C is kept in damp air for a considerable time, it gets covered with a green layer of substance D. Metal A is the best conductor of electricity whereas metal C is the next best conductor of electricity.
(a) What is metal A?
(b) What is metal C?
(c) Name the substance B.
(d) Name the substance D.
Four metals P, Q, R and S are all obtained by the reduction of their oxides with carbon. Metal P is used to form a thin layer over the sheets of metal S to prevent its corrosion. Metal Q is used for electroplating tiffin boxes made of metal S whereas metal R is used in making car batteries. Metals Q and R form an alloy called solder. What are metals P, Q, R and S? How have you arrived at this conclusion?
A black metal oxide XO2 is used as a catalyst in the preparation of oxygen gas from potassium chlorate. The oxide XO2 is also used in ordinary dry cells. The metal oxide XO2 cannot be reduced satisfactorily with carbon to form metal X.
(a) Name the metal X.
(b) Name the metal oxide XO2.
(c) Which reducing agent can be used to reduce XO2 to obtain metal X?
(d) Name another metal which can also be extracted by the reduction of its oxide with the above reducing agent.
Metals X and Y can be recovered from the anode mud left behind after the electrolytic refining of copper metal. The coins made of metal X look new even after several years of use but the coins made of metal Y lose their shine gradually and get blackened soon. When metal X is alloyed with a small amount of metal Y, it becomes hard and hence suitable for making ornaments. What are metals X and Y? Also state the colour of metal X.
Solutions for 3: Metals and Non-metals
![Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals - Shaalaa.com](/images/9352831810-chemistry-science-english-class-10_6:7eeaf5db0f4a49c580d3c8746ff5ab36.jpg)
Lakhmir Singh solutions for Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Metals and Non-metals
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Lakhmir Singh solutions for Mathematics Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 CBSE 3 (Metals and Non-metals) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Lakhmir Singh textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals are Chemical Properties of Metal, Corrosion of Metals, The Covalent Bond, Chemical Properties of Non-metal, Types of Element: Metals, Types of Element: Non-metal, Physical Properties of Metals, Extraction of Reactive Metals, Refining of Metals, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Physical Properties of Non-metal, Reactivity Series of Metals, Prevention of Corrosion.
Using Lakhmir Singh Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 solutions Metals and Non-metals exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Lakhmir Singh Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 students prefer Lakhmir Singh Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Metals and Non-metals Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry (Science) [English] Class 10 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
