Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name one covalent compound containing chlorine.
Solution
A covalent compound that contains chlorine is hydrogen chloride (HCl).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What type of bonds are present in methane (CH4) and sodium chloride (NaCl)?
Fill in the blanks in the following sentence:
In forming oxygen molecule, .............. electrons are shared by each atom of oxygen.
Give two general properties of ionic compounds and two those of covalent compounds.
Draw the electron-dot structure of H2O compound and state the type of bonding.
State one use of diamond which depends on its 'extraordinary brilliance' and one use of graphite which depends on its being 'black and quite soft'.
Describe the structure of graphite with the help of a labelled diagram.
Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity?
One of the following contains a double bond as well as single bonds. This is:
(a) CO2
(b) O2
(c) C2H4
(d) C2H2
Explain the following term with example.
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
The following structural formula belongs to which carbon compound?
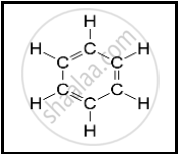
Give examples for the following:
Two gaseous polar compounds.
Compare the compounds carbon tetrachloride and sodium chloride with regard to solubility in water and electrical conductivity.
State the type of bond formed when the combining atom has zero E.N. difference.
Define a covalent bond.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Covalent compounds are generally soluble in _________ solvents.
Write an Explanation.
Alkene
When ethyl alcohol and acetic acid are mixed, the resulting ester has a chemical formula ______.
Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g., hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of ______.
Assertion (A): Melting point and boiling point of ethanol are lower than that of sodium chloride.
Reason (R): The forces of attraction between the molecules of ionic compounds are very strong.
Explain dipole (polar) molecule by taking hydrogen chloride as an example.
