Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name five methods of preventing rusting of iron.
Solution
Five methods of preventing rusting of iron are:
- By polishing the surface of iron with paint
- By applying oil or grease on the surface of iron
- By coating a thin layer of zinc on the iron metal by the process called galvanisation
- By coating other metals like tin coating and chromium coating
- By alloying with other metals (chromium and nickel) to form stainless steel, which does not corrode
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are ______ and ______.
Explain why Iron sheets are coated with zinc during galvanization.
What is anodising? Give its applications.
What is meant by 'rusting of iron'? With the help of labelled diagrams, describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts.
Name two metals which resist corrosion due to the formation of a thin, hard and impervious layer of oxide on their surface.
In stainless steel alloy, iron metal is mixed with:
(a) Cu and Cr
(b) Cr and Ni
(c) Cr and Sn
(d) Cu and Ni
Name the metal which is a constituent of blood pigment?
State under what conditions corrosion is faster ?
Give reason for the following:
A suspension of rust is basic in nature.
Match the columns.
| Group A | Group B |
| 1) Electroplating | a) Pressure cooker |
| 2) Anodising | b) Silver plated spoons |
| c) Coating of tin on copper | |
| d) Coating of Zinc on iron |
Write scientific reason.
On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
What is rust?
Observe the following diagram and give answers.
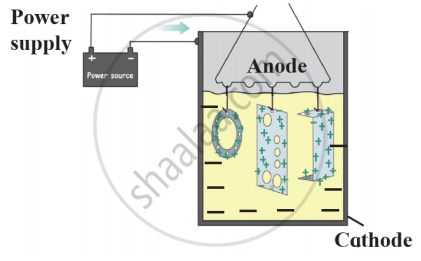
- Name this method of prevention of corrosion.
- For prevention of which metal this method is used?
- What is used as anode in this method?
Observe the following figure and write the answer of the question.

- Which process is shown in the figure?
- Explain the chemical reaction shown in the figure.
- Write the reactions on anode and cathode.
The diagram shows the reaction between metal and dil. acid.
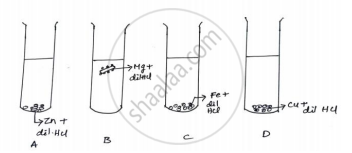
What is the reason for different behaviour of Mg in test tube B?
Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated but when metals (except Mn and Mg), treated with HNO3, hydrogen is not liberated, why?
Give an example of a chemical reaction for each of the following situations:
Sound is produced
Gold plated ornaments is the example of ______.
Explain the chemical reactions in rusting of iron.
