Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
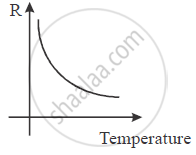
How does the resistivity of a semiconductor change with rise of temperature ? Explain.
उत्तर
As the temperature increase number of charge particle (holes and electrons) also increases. So, current increase and resistance decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A negligibly small current is passed through a wire of length 15 m and uniform cross-section 6.0 × 10−7 m2, and its resistance is measured to be 5.0 Ω. What is the resistivity of the material at the temperature of the experiment?
Two resistors A and B have resistances RA and RB, respectively, and RA < RB. The resistivities of their materials are ρA and ρB.
A uniform wire of resistance 100 Ω is melted and recast as a wire whose length is double that of the original. What would be the resistance of the wire?
The electrochemical equivalent of a material depends on _______________ .
Choose the correct alternative:
The resistivity of the alloy manganin is nearly independent of/increases rapidly with increase of temperature.
Choose the correct alternative:
The resistivity of a typical insulator (e.g., amber) is greater than that of a metal by a factor of the order of (1022/1023).
If the last band on the carbon resistor is absent, then the tolerance is ______
