Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
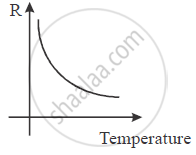
How does the resistivity of a semiconductor change with rise of temperature ? Explain.
Solution
As the temperature increase number of charge particle (holes and electrons) also increases. So, current increase and resistance decreases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What conclusion can you draw from the following observations on a resistor made of alloy manganin?
| Current A |
Voltage V |
Current A |
Voltage V |
| 0.2 | 3.94 | 3.0 | 59.2 |
| 0.4 | 7.87 | 4.0 | 78.8 |
| 0.6 | 11.8 | 5.0 | 98.6 |
| 0.8 | 15.7 | 6.0 | 118.5 |
| 1.0 | 19.7 | 7.0 | 138.2 |
| 2.0 | 39.4 | 8.0 | 158.0 |
A heating element is marked 210 V, 630 W. What is the value of the current drawn by the element when connected to a 210 V dc source?
A uniform wire of resistance 100 Ω is melted and recast as a wire whose length is double that of the original. What would be the resistance of the wire?
If R1 and R2 are filament resistances of a 200 W and a 100 W bulb respectively, designed to operate on the same voltage, then:
Choose the correct alternative:
Alloys usually have much (lower/higher) temperature coefficients of resistance than pure metals.
Choose the correct alternative:
The resistivity of the alloy manganin is nearly independent of/increases rapidly with increase of temperature.
The resistivity of alloy manganin is ______.
Fuse wire should have
If the last band on the carbon resistor is absent, then the tolerance is ______
