Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2018-2019
Date & Time: 5th March 2019, 2:30 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
Define the term 'intensity of radiation' in terms of photon picture of light.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
State the condition under which a large magnification can be achieved in an astronomical telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced by red light? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Show variation of resistivity of copper as a function of temperature in a graph.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two metallic spheres A and B kept on insulating stands are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod P is brought near the sphere A as shown in the figure. The two spheres are separated from each other, and the rod P is removed. What will be the nature of charges on spheres A and B?
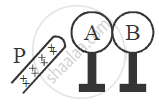
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A metal sphere is kept on an insulting stands. A negatively charged rod is brought near it, then the sphere is earthed as shown. On removing the earthing, and taking the negatively charged rod away, what will be the nature of charge on the sphere? Give reason for your answer.
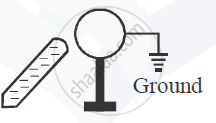
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Write the function of receiver in communication system.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Plot a graph showing the variation of undecayed nuclei N versus time t. From the graph, find out how one can determine the half-life and average life of the radioactive nuclei.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Which property of nuclear force explains the constancy of binding energy per nucleon
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Complete the following nuclear reactions :
(i)
(ii)
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Obtain Bohr’s quantisation condition for angular momentum of electron orbiting in nth orbit in hydrogen atom on the basis of the wave picture of an electron using de Broglie hypothesis.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
The figure show a network of five capacitors connected to a 10V battery. Calculate the charge acquired by the 5μF capacitor.
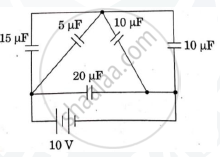
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
A .0.5m long solenoid of 10 turns/cm has area of cross-section 1cm2 . Calculate the voltage induced across its ends if the current in the solenoid is changed from 1A to 2A in 0.1s.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A small flat search coil of area 5cm2 with 140 closely wound turns is placed between the poles of a powerful magnet producing magnetic field 0.09T and then quickly removed out of the field region. Calculate:
(a) Change of magnetic flux through the coil, and
(b) emf induced in the coil.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
In the case of a concave mirror of focal length f , when an object is kept between f and 2 f , show that its image is formed beyond 2 f .
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Five point charges, each of charge +q are placed on five vertices of a regular hexagon of side 'l '. Find the magnitude of the resultant force on a charge -q placed at the centre of the hexagon.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A smple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
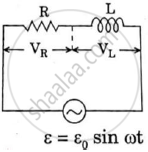
An ac circuit as shown in the figure has an inductor of inductance L and a resistor or resistance R connected in series. Using the phasor diagram, explain why the voltage in the circuit will lead the current in phase.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
The potential difference across the resistor is 160V and that across the inductor is 120V. Find the effective value of the applied voltage. If the effective current in the circuit be 1.0 A, calculate the total impedance of the circuit.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
An ac circuit consists of a series combination of circuit elements X and Y. The current is ahead of the voltage in phase by
(a) name the circuit element Y.
(b) calculate the rms value of current, if rms value of voltage is 141V.
(c) what will happen if the ac source is replaced by a dc source ?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Write the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic radiations:
(a) Infrared rays
(b) Ultraviolet rays
(c) γ -rays
Write one use of each of the above.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Advertisements
Plot a graph to show the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation in relation to photoelectric effect.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Use Einstein’s photoelectric equation to show how from this graph,
(i) Threshold frequency, and (ii) Planck’s constant can be determined.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
How does one explain the emission of electrons from a photosensitive surface with the help of Einstein’s photoelectric equation?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Work function of aluminium is 4.2 eV. If two photons each of energy 2.5 eV are incident on its surface, will the emission of electrons take place? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted? Calculate in Joules.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Explain how an unpolarised light gets polarised when incident on the interface separating the two transparent media.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Green light is incident at the polarising angle on a certain transparent medium. The angle of refraction is 30° . Find
(i) polarising angle, and
(ii) refractive index of the medium.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the value of the current shown in the ammeter A.
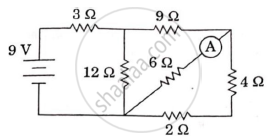
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Explain briefly, using a proper diagram, the difference in behaviour of a conductor and a dielectric in the presence of external electric field.
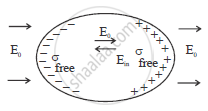
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Define the term polarization of a dielectric and write the expression for a linear isotropic dielectric in terms of electric field.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Obtain the expression for the current flowing through a conductor having number density of the electron n, area of cross-section A in terms of the drift velocity vd .
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
How does the resistivity of a semiconductor change with rise of temperature ? Explain.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
(i) Write the truth tables of the logic gates marked P and Q in the given circuit.
(ii) Write the truth table for the circuit.
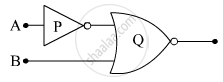
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Why are NOR gates considered as universal gates?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Explain how a potential barrier is developed in a p-n junction diode.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in reverse bias. Plot the V-I characteristics in this case.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
How are eddy currents generated in a conductor which is subjected to a magnetic field?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Write two examples of their useful applications .
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
How can the disadvantages of eddy currents be minimized?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Advertisements
A converging beam of light travelling in air converges at a point P as shown in the figure. When a glass sphere of refractive index 1 . 5 is introduced in between the path of the beam, calculate the new position of the image. Also draw the ray diagram for the image formed.
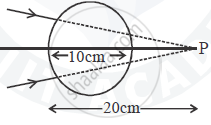
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A point ‘O’ marked on the surface of a glass sphere of diameter 20 cm is viewed through glass from the position directly opposite to the point O. If the refractive index of the glass is 1.5, find the position of the image formed. Also, draw the ray diagram for the formation of the image.
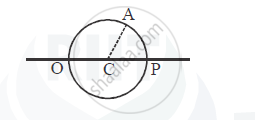
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
What do you mean by bandwidth of a signal? Give its importance.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Differentiate between Analog and Digital communication.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Answer the following question :
Write the functions of transducer and repeater ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Define the dipole moment of a magnetic dipole. Write its S.I. unit.
Obtain the expression for the torque acting on a magnetic dipole placed in an external unifrom magnetic field.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Draw a circuit diagram of an n-p-n transistor with its emitter-base junction forward biased and basecollector junction reverse biased. Briefly describe its working.
Explain how a transistor in its active state exhibits a low resistance at its emitter-base junction and high resistance at its base-collector junction.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Derive the expression for the voltage gain of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration in terms of the load resistance RL, current gain a βa and input resistance.
Explain why input and output voltages are in opposite phase.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the V-I characteristics of an LED. State two advantages of LED lamps over convertional incandescent lamps.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
State and explain the law used to determine magnetic field at a point due to a current element. Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a circular current carrying loop of radius r at its centre.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A long wire with a small current element of length 1 cm is placed at the origin and carries a current of 10 A along the X-axis. Find out the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field due to the element on the Y-axis at a distance 0.5 m from it.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a current carrying coil of radius r at a distance x from the centre along the X-axis.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A straight wire carrying a current of 5 A is bent into a semicircular arc of radius 2 cm as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the centre of the arc.

Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Can the interference pattern be produced by two independent monochromatic sources of light? Explain.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
The intensity at the central maximum (O) in a Young’s double slit experimental set-up shown in the figure is IO. If the distance OP equals one-third of the fringe width of the pattern, show that the intensity at point P, would equal

Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In Young’s double slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0.5 mm and screen is placed 1.0 m away from the slit. It is found that the 5th bright fringe is at a distance of 4.13 mm from the 2nd dark fringe. Find the wavelength of light used.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Derive the relation a sin θ = λ for the first minimum of the diffraction pattern produced due to a single slit of width ‘a’ using light of wavelength λ.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
State with reason, how the linear width of the central maximum will be affected if
(i) monochromatic yellow light is replaced with red light, and
(ii) distance between the slit and the screen is increased.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Using the monochromatic light of same wavelength in the experimental set-up of the diffraction pattern as well as in the interference pattern where the slit separation is 1 mm, 10 interference fringes are found to be within the central maximum of the diffraction pattern. Determine the width of the single slit, if the screen is kept at the same distance from the slit in the two cases.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2018 - 2019
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2019 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
