Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted? Calculate in Joules.
Solution 1
We know that KEmax = eV0
V0 = 1.5V
= 1.6 × 10-19 × 1.5
= 2.4 × 10-19 J
KE = 2.4 × 10-19 J
Solution 2
Using Einstein's photoelectric equation,
`("K.E".)_"max" = "hv" - phi = "h"("v" - "v"_@)`
⇒ `("K.E".)_"max" = "h"("v" - "v"_@) = "eV"_@`
Where Vo is the stopping potential.
According to the given data, Vo = 1.5 V
Hence,
`(K.E.)_"max" = "eV"_@ = "e" xx 1.5 "V" = 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 1.5 "Joules")`
(K.E.)max = 2.4 × 10-19 Joules
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is so special about the combination e/m? Why do we not simply talk of e and m separately?
Visible light has wavelengths in the range of 400 nm to 780 nm. Calculate the range of energy of the photons of visible light.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A photographic film is coated with a silver bromide layer. When light falls on this film, silver bromide molecules dissociate and the film records the light there. A minimum of 0.6 eV is needed to dissociate a silver bromide molecule. Find the maximum wavelength of light that can be recorded by the film.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A light beam of wavelength 400 nm is incident on a metal plate of work function 2.2 eV. (a) A particular electron absorbs a photon and makes two collisions before coming out of the metal. Assuming that 10% of the extra energy is lost to the metal in each collision, find the kinetic energy of this electron as it comes out of the metal. (b) Under the same assumptions, find the maximum number of collisions the electron can suffer before it becomes unable to come out of the metal.
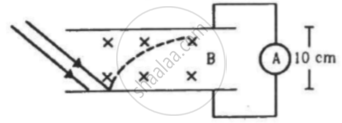
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the emitter and the collector plates are placed at a separation of 10 cm and are connected through an ammeter without any cell. A magnetic field B exists parallel to the plates. The work function of the emitter is 2.39 eV and the light incident on it has wavelengths between 400 nm and 600 nm. Find the minimum value of B for which the current registered by the ammeter is zero. Neglect any effect of space charge.
Plot a graph to show the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation in relation to photoelectric effect.
For a given frequency of light and a positive plate potential in the set up below, If the intensity of light is increased then ______.
When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W/m2 falls on a platinum surface of area 1.0 × 10-4 m2, only 53% of the incident photons eject photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is ______.
The electromagnetic theory of light failed to explain ______.
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current
