Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted? Calculate in Joules.
उत्तर १
We know that KEmax = eV0
V0 = 1.5V
= 1.6 × 10-19 × 1.5
= 2.4 × 10-19 J
KE = 2.4 × 10-19 J
उत्तर २
Using Einstein's photoelectric equation,
`("K.E".)_"max" = "hv" - phi = "h"("v" - "v"_@)`
⇒ `("K.E".)_"max" = "h"("v" - "v"_@) = "eV"_@`
Where Vo is the stopping potential.
According to the given data, Vo = 1.5 V
Hence,
`(K.E.)_"max" = "eV"_@ = "e" xx 1.5 "V" = 1.6 xx 10^-19 xx 1.5 "Joules")`
(K.E.)max = 2.4 × 10-19 Joules
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is the formula you employ in (a) valid for calculating radius of the path of a 20 MeV electron beam? If not, in what way is it modified?
Visible light has wavelengths in the range of 400 nm to 780 nm. Calculate the range of energy of the photons of visible light.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Two neutral particles are kept 1 m apart. Suppose by some mechanism some charge is transferred from one particle to the other and the electric potential energy lost is completely converted into a photon. Calculate the longest and the next smaller wavelength of the photon possible.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A photographic film is coated with a silver bromide layer. When light falls on this film, silver bromide molecules dissociate and the film records the light there. A minimum of 0.6 eV is needed to dissociate a silver bromide molecule. Find the maximum wavelength of light that can be recorded by the film.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on a cesium plate at the rate of 5.0 W. The potential of the collector plate is made sufficiently positive with respect to the emitter, so that the current reaches its saturation value. Assuming that on average, one out of every 106 photons is able to eject a photoelectron, find the photocurrent in the circuit.
In the arrangement shown in the figure, y = 1.0 mm, d = 0.24 mm and D = 1.2 m. The work function of the material of the emitter is 2.2 eV. Find the stopping potential V needed to stop the photocurrent.
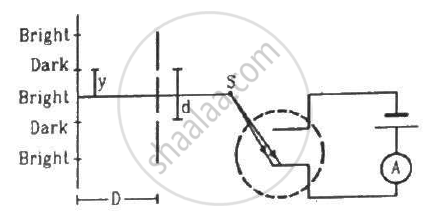
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Work function of aluminium is 4.2 eV. If two photons each of energy 2.5 eV are incident on its surface, will the emission of electrons take place? Justify your answer.
In the case of a photo electric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The wave theory of light could not explain the existence of the threshold frequency.
For a given frequency of light and a positive plate potential in the set up below, If the intensity of light is increased then ______.
When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W/m2 falls on a platinum surface of area 1.0 × 10-4 m2, only 53% of the incident photons eject photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is ______.
