Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A .0.5m long solenoid of 10 turns/cm has area of cross-section 1cm2 . Calculate the voltage induced across its ends if the current in the solenoid is changed from 1A to 2A in 0.1s.
Solution
l = 0. 5m
n = 10 turns /cm = 10 × 10+2 turns/ m
a = 1 cm2 = 10-4
`(di)/(dt) = (2-1)/0.1 = 1/(0.1) = 10 `A / s
`ε = -L (di)/(dt)`
` = mu_0 n^2 Al (di)/(dt)`
= 4π × 10-7 × (10+3)2 × 10-4 × 0.5 × 10
= 4π × 10-7 × 106 × 10-4 × 5 × 10-1 × 10
ε = 20π × 10-5 V
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A jet plane is travelling towards west at a speed of 1800 km/h. What is the voltage difference developed between the ends of the wing having a span of 25 m, if the Earth’s magnetic field at the location has a magnitude of 5 × 10−4 T and the dip angle is 30°.
State Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
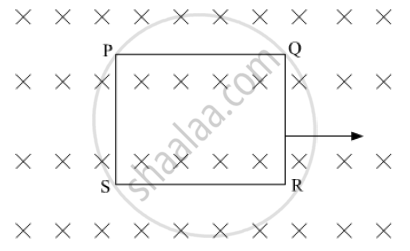
The closed loop (PQRS) of wire is moved into a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the plane of the paper as shown in the figure, Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop.
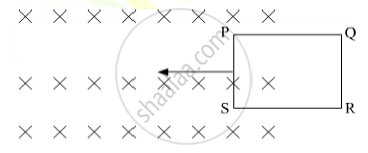
The closed loop (PQRS) of wire is moved into a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the plane of the paper as shown in the figure. Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop.
The two rails of a railway track, insulated from each other and the ground, are connected to millivoltmeter. What is the reading of the millivoltmeter when a train passes at a speed of 180 km/hr along the track, given that the vertical component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.2 × 10–4 wb/m2 and rails are separated by 1 metre ______.
Faraday’s laws are consequence of the conservation of ______.
The average e.m.f induced in a coil in which current change from 0.2 ampere to 0.4 ampere in· 0.1 sec is 1 volt, the self-inductance of the coil is
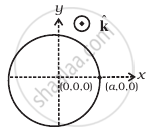
A magnetic field in a certain region is given by `B = B_o cos (ωt)hatk` and a coil of radius a with resistance R is placed in the x-y plane with its centre at the origin in the magnetic field (Figure) . Find the magnitude and the direction of the current at (a, 0, 0) at t = π/2ω, t = π/ω and t = 3π/2ω.
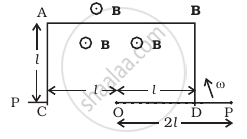
ODBAC is a fixed rectangular conductor of negilible resistance (CO is not connnected) and OP is a conductor which rotates clockwise with an angular velocity ω (Figure). The entire system is in a uniform magnetic field B whose direction is along the normal to the surface of the rectangular conductor ABDC. The conductor OP is in electric contact with ABDC. The rotating conductor has a resistance of λ per unit length. Find the current in the rotating conductor, as it rotates by 180°.
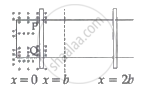
The arm PQ of a rectangular conductor is moving from x = 0 to x = 2b outwards and then inwards from x = 2b to x = 0 as shown in the figure. A uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane is acting from x = 0 to x = b. Identify the graph showing the variation of different quantities with distance.