Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A straight wire carrying a current of 5 A is bent into a semicircular arc of radius 2 cm as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the centre of the arc.

Solution
Current I = 5A, radius r = 2 cm = 2 x 10-2 m, Number of turns = N = 1/2
So, magnetic field due to semi-circular arc is
`b = (mu_0 NI)/(2r) = (4 pi xx 10^(-7) xx 0.5 xx5)/(2 xx 2 xx 10^(-2)) T = 7.85 xx 10^(-5) T `
The magnetic field due to the straight part of the wire is zero at the centre as its line intersects the centre.
Hence net magnetic field = 7.85×10-5T
The direction of the this magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the paper and directed inside .
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Using Biot − Savart’s law, derive the expression for the magnetic field in the vector form at a point on the axis of a circular current loop?
State Biot-Savart law.
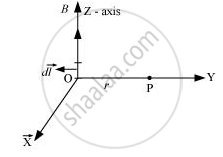
A current I flows in a conductor placed perpendicular to the plane of the paper. Indicate the direction of the magnetic field due to a small element d `vecl` at point P situated at distance `vecr` from the element as shown in the figure.
A proton goes undeflected in a crossed electric and magnetic field (the fields are perpendicular to each other) at a speed of 2.0 × 105 m s−1. The velocity is perpendicular to both the fields. When the electric field is switched off, the proton moves along a circle of radius 4.0 cm. Find the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
A long, vertical wire carrying a current of 10 A in the upward direction is placed in a region where a horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 2.0 × 10−3 T exists from south to north. Find the point where the resultant magnetic field is zero.
A wire of length l is bent in the form of an equilateral triangle and carries an electric current i. (a) Find the magnetic field B at the centre. (b) If the wire is bent in the form of a square, what would be the value of B at the centre?
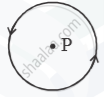
An electric current I flows through a circular loop as shown in Figure 2(b) below. Write an expression and direction for the magnetic field at the centre of the loop at point P.
Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a current-carrying coil of radius r at a distance x from the center along the X-axis.
- both are long range and inversely proportional to the square of distance from the source to the point of interest.
-
both are linear in source.
-
both are produced by scalar sources.
-
both follow principle of superposition.
A circular loop of radius 0.3 cm lies parallel to much bigger circular of radius 20 cm. The centre of the small loop is on the axis of the bigger loop. The distance between their centres is 15 cm. If a current of 2.0 A flows through the smaller loop, then the flux linked with the bigger loop is ______.
