Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How good is the system of G.S.T as compared to the old tax system?
उत्तर
The system of G.S.T is good as compared to the old tax system in the following ways:
- Abolition of different tax structures - The implementation of GST resulted in the abolition of state-imposed taxes such as value-added tax, entry tax, octroi, and luxury tax as well as service tax, union excise duty, central sales tax (collected by states), and customs duty. Cess, resale, extra, and turnover taxes, among others, have all been abolished.
- Widening of tax bases - The GST has broadened governments' tax bases. Government administrative expenses have decreased as a result.
- The benefit of Input tax credit - Every stage, whether for the manufacturer, middleman or end user, is subject to the GST levy. The assessee benefits from an input tax credit side by side, which means he simply has to pay the difference between output tax and input tax. As a result, GST has eliminated the tax's cascading effect, following in the footsteps of VAT.
- Neutralization to process, business models, structure, and location - Because of the neutrality of the tax regime, GST is expected to improve economic development, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Because of the lessened effect of tariffs on numerous commodities, GST may contribute to an increase in exports, giving exporters an advantage over their competition in the worldwide market.
- Increased demand and production of goods and services - Because of the GST's lower production costs, manufacturing facilities would grow and there would be more demand for goods and services.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fiscal deficit equals :
(a) Interest payments
(b) Borrowings
(c) Interest payments less borrowing
(d) Borrowing less interest payments
Explain 'Revenue Deficit in a Government budget? What does it indicate?
Define fiscal deficit
Define revenue
Give the relationship between the revenue deficit and the fiscal deficit.
Suppose that for a particular economy, investment is equal to 200, government purchases are 150, net taxes (that is lump-sum taxes minus transfers) is 100 and consumption is given by C = 100 + 0.75Y (a) What is the level of equilibrium income? (b) Calculate the value of the government expenditure multiplier and the tax multiplier. (c) If government expenditure increases by 200, find the change in equilibrium income.
We suppose that C = 70 + 0.70Y D, I = 90, G = 100, T = 0.10Y (a) Find the equilibrium income. (b) What are tax revenues at equilibrium Income? Does the government have a balanced budget?
Explain the relation between government deficit and government debt.
Answer the following question.
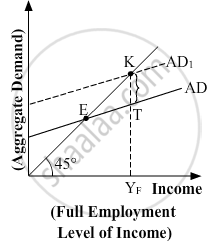
In the given figure, what does the gap 'KT' represent? State any two fiscal measures to correct the situation.
Regressive tax is that which is ______.
| S. No. | Content | Rs (in crores) |
| 1. | Revenue Expenditure | 100 |
| 2. | Capital Receipts | 40 |
| 3. | Net Borrowings | 38 |
| 4. | Net Interest Payments | 27 |
| 5. | Tax Revenue | 50 |
| 6. | Non-tax Revenue | 15 |
Which of the following is the formula for revenue deficit?
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1: Fiscal Deficit = Total Budget Expenditure - Total Budget Receipts (Net of borrowing)
Statement 2: Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit + Interest Payments.
When the revenue receipts are less than the revenue expenditures in a government budget, this shortfall is termed as
______ in the budget is an important measure of deficit.
______ are the transactions between the residents of two countries that take place due to consideration of profit.
Which of the following transactions are correct about ORT?
Primary deficit is borrowing requirements of government for making:
The shape of average revenue curve in monopoly is ______
On the basis of the given information, calculate the value of:
- Fiscal deficit
- Primary deficit
| S.No. | Items | 2021-22 (₹ in crore) |
| (i) | Revenue Receipts | 20 |
| (ii) | Capital Expenditure | 15 |
| (iii) | Revenue Deficit | 10 |
| (iv) | Non-debt creating capital receipts | 50% of revenue receipts |
| (v) | Interest Payments | 4 |
