Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How will you represent first order reactions graphically.
उत्तर
i. The differential rate law for the first-order reaction A → P is 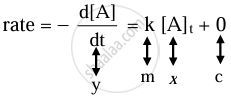
The equation is of the form y = mx + c. A plot of rate versus [A]t is a straight line passing through the origin. The slope of straight line = k.
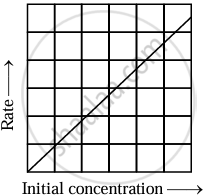 |
| Variation of rate with [A] |
ii. The integrated rate law is
k = `2.303/t log_10 ["A"]_0/["A"]_"t"`
On rearrangement, the equation becomes
`(kt)/2.303 = log_10 ["A"]_0 - log_10 ["A"]_"t"`
Hence,
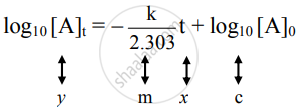
The equation is of the straight line. A graph of `log_10[A]_t` versus t yields a straight line with slope `-"k"/2.303` and y-axis intercepts as log10[A]0.
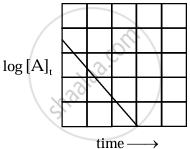 |
| Variation of `log_10 [A]_t` with time |
iii. Rearranging the integrated rate law equation, we get
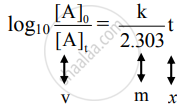
The equation has a straight-line form y = mx. Hence, the graph of `log_10 ([A]_0)/([A]_t)` versus t is a straight line passing through the origin.
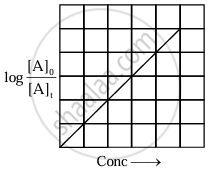 |
| Variation of `log_10 ([A]_0)/([A]_t)` with time |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
How do the half-lives of the first order and zero-order reactions change with the initial concentration of reactants?
Answer the following in brief.
Derive the integrated rate law for the first-order reaction.
Answer the following in brief.
Derive the integrated rate law for the first-order reaction,
\[\ce{A_{(g)} -> B_{(g)} + C_{(g)}}\] in terms of pressure.
Answer the following in brief.
What is a zeroth-order reaction?
Rate constant of a reaction is 3.6 × 10–3 s–1. The order of reaction is ______.
Write order of the following reaction:
\[\ce{2NH_{3(g)} -> N_{2(g)} + 3H_{2(g)}}\]
Derive an integrated rate law expression for first order reaction: A → B + C
The rate constant of the first order reaction is 1.386 min–1. Calculate the time required for 80% reactant to decompose?
Define half life of a reaction.
For a first-order reaction \[\ce{A -> B}\] the rate constant is x min−1. If the initial concentration of A is 0.01 M, the concentration of A after one hour is given by the expression.
For a first-order reaction, the rate constant is 6.909 min−1 the time taken for 75% conversion in minutes is
The rate constant of a reaction is 5.8 × 10−2 s−1. The order of the reaction is ____________.
Write the rate law for the following reaction.
A reaction that is `3/2` order in x and zero order in y.
The rate of the reaction \[\ce{A + B -> C}\] is 3.6 × 10−2 mol dm−3 s−1 when [A] = 0.3 mol dm−3 and [B] = 0.2 mol dm−3. Calculate k if reaction is first order in A and zero order in B.
The rate constant of a reaction has same units as the rate of reaction. The reaction is of ____________.
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant, decreases from 0.8 mol dm−3 to 0.4 mol dm−3 in 15 minutes. The time taken for the concentration to change from 0.1 mol dm−3 to 0.025 mol dm−3 is ____________.
In a first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant is reduced to 25% in one hour. The half-life period of the reaction is ____________.
If time required to decrease concentration of reactant from 0.8 M to 0.2 M is 12 hours, the half life of this first order reaction is ____________.
For first order reaction the slope of the graph of log10 [A]t Vs. time is equal to ____________.
A first order reaction takes 40 minutes for 30% decomposition. What is the half-life of reaction?
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 16 minutes. The percentage of reactant that will react in 32 minutes is ____________.
For zero order reaction, when [A]t is plotted against time (t), the slope of the straight line obtained is equal to ______.
The integrated rate equation is Rt = log C0 – log Ct, then the straight-line graph is obtained by plotting.
The integrated rate law is a direct relationship between time and ______
The rate constant and half-life of a first order reaction are related to each other as ______.
Which among the following reactions is an example of pseudo first order reaction?
Consider the following reaction.
\[\ce{SO2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) <=>[K1] SO3(g)}\]
\[\ce{2SO3(g)<=>[K2] 2SO2(g) + O2(g)}\]
What is the relation between K1 and K2?
A radioactive isotope decayed to 17/32 of its original mass after 60 minutes. Find the half-life of this radioisotope.
The half-life period for the first order reaction is 1.7 hrs. How long will it take for 20% of the reactant to disappear?
