Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If a light ray does not undergo, refraction at the boundary between two media, the angle of incidence is:
विकल्प
0°
45°
60°
90°
उत्तर
0°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light travels from water to air as shown in the diagram given below :

1) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the way. Given the critical angle for water is 48°.
2) State the condition so that internal reflection occurs in the above diagram.
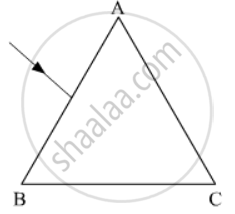
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index`3/2`, placed in water of refractive index `4/3`.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
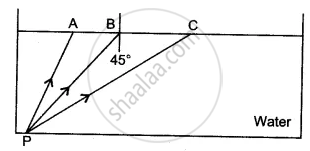
The diagram shows a point source P inside a water container. Three rays A, B, and C starting from P are shown up to the water surface. Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for the water-air pair is 48°.
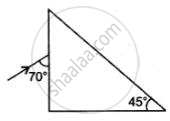
Complete the following diagram to show the path of the ray of a single colour in the diagram as if enters in and emerges out of the prism. Mark the angles wherever necessary. (Critical angle for glass = 42°).
Answer the following question.
Explain ‘mirage’ as an illustration of refraction.
Answer the following question.
Under what conditions are total internal reflection possible? Explain it with a suitable example.
Total internal reflection can take place only if light is travelling from ______.
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB (Figure). When observed from the face AD, the pin shall ______.
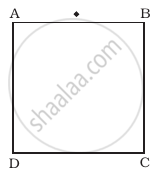
- appear to be near A.
- appear to be near D.
- appear to be at the centre of AD.
- not be seen at all.
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index µ, the angle of incidence is found to be twice the angle of refraction. Then the angle of incidence is ______.
State two differences between normal reflection and total internal reflection.
