Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
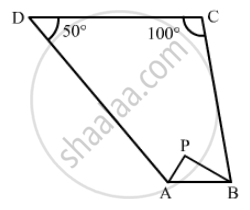
In Fig. 16.21, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B meet at a point P. If ∠C = 100° and ∠D = 50°, find the measure of ∠APB.
उत्तर
\[∠A + ∠B + ∠C +∠D = 360° \]
\[ \Rightarrow ∠A +∠B + 100°+ 50° = 360° \]
\[ \Rightarrow ∠A + ∠B = 210° . . . (i)\]
\[\text{ In } \bigtriangleup APB, \text{ we have } : \]
\[\frac{1}{2}∠A + \frac{1}{2}∠B + ∠APB = 180° \]
\[ \Rightarrow ∠APB = 180° - \frac{1}{2}\left( ∠A + ∠B \right)\]
\[\text{ From (i), we get: } \]
\[ \Rightarrow ∠APB = 180° - \left( \frac{1}{2} \times 210° \right) \]
\[ \therefore ∠APB = 75° \]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term Quadrilateral .
The four angles of a quadrilateral are as 3 : 5 : 7 : 9. Find the angles.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the angles A, B, C and D are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 4 : 5. Find the measure of each angle of the quadrilateral.
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium. Find the values of x and y.

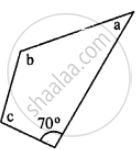
In the given figure : ∠b = 2a + 15 and ∠c = 3a + 5; find the values of b and c.
Two diagonals of an isosceles trapezium are x cm and (3x – 8) cm. Find the value of x.
If three angles of a quadrilateral are 90° each, show that the given quadrilateral is a rectangle.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
Three angles of a quadrilateral are 75º, 90º and 75º. The fourth angle is ______.
If bisectors of ∠A and ∠B of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at P, of ∠B and ∠C at Q, of ∠C and ∠D at R and of ∠D and ∠A at S, then PQRS is a ______.
