Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
उत्तर
Ea = 52897.78 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
Consider figure and mark the correct option.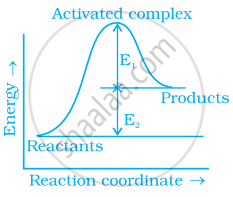
Mark the incorrect statements:
(i) Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to reaction mechanism.
(ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy.
(iii) Catalyst lowers the activation energy.
(iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction.
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
The activation energy of one of the reactions in a biochemical process is 532611 J mol–1. When the temperature falls from 310 K to 300 K, the change in rate constant observed is k300 = x × 10–3 k310. The value of x is ______.
[Given: ln 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J K–1 mol–1]
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
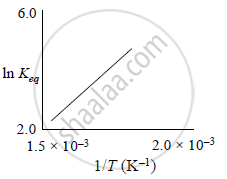
The reaction must be:
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
