Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
What is the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a reaction? How can this effect of temperature on rate constant be represented quantitatively?
उत्तर
The rate constant of a reaction is nearly doubled with a 10° rise in temperature. However, the exact dependence of the rate of a chemical reaction on temperature is given by Arrhenius equation,
`k = Ae^(-E_a/(RT))`
Where,
A is the Arrhenius factor or the frequency factor
T is the temperature
R is the gas constant
Ea is the activation energy
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10−2 to 8 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea). (log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ of ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half life period be 10 minutes?
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1]
Define activation energy.
Explain the following terms :
Half life period of a reaction (t1/2)
The chemical reaction in which reactants require high amount of activation energy are generally ____________.
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ______.
Consider figure and mark the correct option.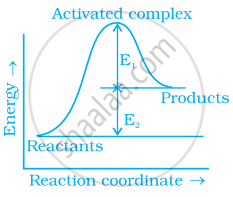
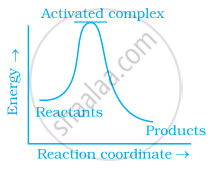
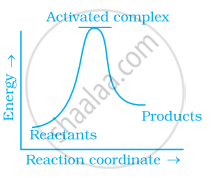
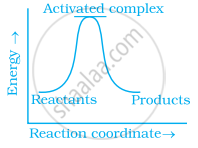
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
(b)
(c)
The reaction between \[\ce{H2(g)}\] and \[\ce{O2(g)}\] is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example.
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
The activation energy of one of the reactions in a biochemical process is 532611 J mol–1. When the temperature falls from 310 K to 300 K, the change in rate constant observed is k300 = x × 10–3 k310. The value of x is ______.
[Given: ln 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J K–1 mol–1]
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
The decomposition of N2O into N2 and O2 in the presence of gaseous argon follows second-order kinetics, with k = (5.0 × 1011 L mol−1 s−1) `"e"^(-(29000 "K")/"T")`. Arrhenius parameters are ______ kJ mol−1.
