Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ______.
विकल्प
determining the rate constant at standard temperature.
determining the rate constants at two temperatures.
determining probability of collision.
using catalyst.
उत्तर
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by determining the rate constants at two temperatures.
Explanation:
`log k_2/k_1 = E_a/(2.303R)(1/T_1 - 1/T_2)`
Where, Ea = activation energy
T2 = higher temperature
T1 = lower temperature
k1 = rate constant at temperature T1
k2 = rate constant at temperature T2
This equation is known as Arrhenius equation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10−2 to 8 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea). (log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Consider a certain reaction \[\ce{A -> Products}\] with k = 2.0 × 10−2 s−1. Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100 s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L−1.
During decomposition of an activated complex:
(i) energy is always released
(ii) energy is always absorbed
(iii) energy does not change
(iv) reactants may be formed
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
(iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
(iv) Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change ΔE during the reaction is - 20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is ______.
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
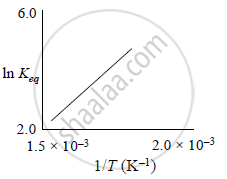
The reaction must be:
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased? Justify.
