Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During decomposition of an activated complex:
(i) energy is always released
(ii) energy is always absorbed
(iii) energy does not change
(iv) reactants may be formed
उत्तर
(i) energy is always released
(iv) reactants may be formed
Explanation:
Activation Energy is the amount of energy released when reactant molecules collide and form an activated complex. When energy is released, the complex decomposes into a product.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 × 10−2 to 4 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Consider a certain reaction \[\ce{A -> Products}\] with k = 2.0 × 10−2 s−1. Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100 s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L−1.
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Predict the main product of the following reactions: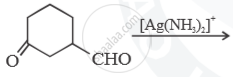
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
(b)
(c)
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) Rate of a reaction increases with decrease in activation energy.
(iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increase in temperature.
(iv) Rate of reaction decreases with decrease in activation energy.
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
For an endothermic reaction energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction ΔH (both of there in KJ moI–1) minimum value of Ea will be
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
