Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
उत्तर

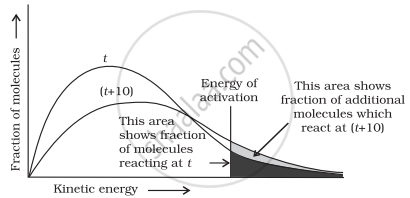
When the temperature is raised’ the maxima of the curve moves to the higher energy value and the curve broadens out so that there is a greater proportion of the molecules with much higher energies. Most probable kinetic energy increases with increase in temperature. As the temperature increases, activation energy decreases which will result in the increase in the rate of reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
Mark the incorrect statements:
(i) Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to reaction mechanism.
(ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy.
(iii) Catalyst lowers the activation energy.
(iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction.
For an endothermic reaction energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction ΔH (both of there in KJ moI–1) minimum value of Ea will be
The slope of Arrhenius Plot `("In" "k" "v"//"s" 1/"T")` of first-order reaction is −5 × 103 K. The value of Ea of the reaction is. Choose the correct option for your answer. [Given R = 8.314 JK−1mol−1]
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change ΔE during the reaction is - 20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is ______.
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
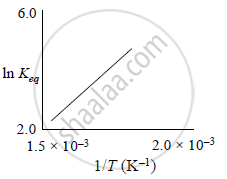
The reaction must be:
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased? Justify.
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
