Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
उत्तर

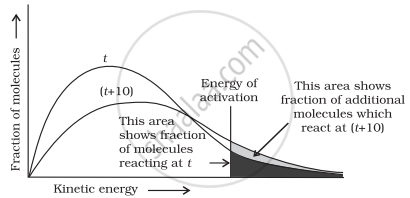
When the temperature is raised’ the maxima of the curve moves to the higher energy value and the curve broadens out so that there is a greater proportion of the molecules with much higher energies. Most probable kinetic energy increases with increase in temperature. As the temperature increases, activation energy decreases which will result in the increase in the rate of reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
(b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
`logk=logA-E_a/2.303R(1/T)`
Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for `logk Vs. 1/T` a straight line with a slope of −4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction.(R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1)
The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below:
| T/°C | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| 105 × k/s−1 | 0.0787 | 1.70 | 25.7 | 178 | 2140 |
Draw a graph between ln k and `1/"T"` and calculate the values of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30º and 50ºC.
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ of ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half life period be 10 minutes?
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1]
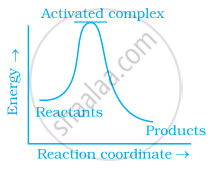
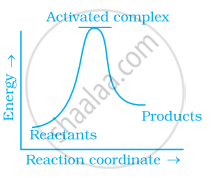
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
(b)
(c)
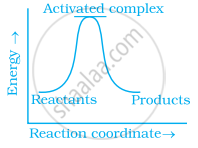
During decomposition of an activated complex:
(i) energy is always released
(ii) energy is always absorbed
(iii) energy does not change
(iv) reactants may be formed
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
In respect of the eqn k = \[\ce{Ae^{{-E_a}/{RT}}}\] in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statement is correct?
The decomposition of N2O into N2 and O2 in the presence of gaseous argon follows second-order kinetics, with k = (5.0 × 1011 L mol−1 s−1) `"e"^(-(29000 "K")/"T")`. Arrhenius parameters are ______ kJ mol−1.
