Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
Solution

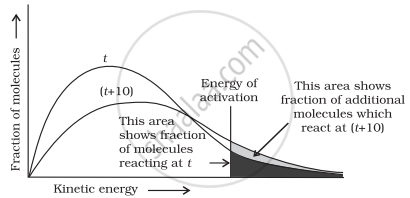
When the temperature is raised’ the maxima of the curve moves to the higher energy value and the curve broadens out so that there is a greater proportion of the molecules with much higher energies. Most probable kinetic energy increases with increase in temperature. As the temperature increases, activation energy decreases which will result in the increase in the rate of reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The rate of the chemical reaction doubles for an increase of 10 K in absolute temperature from 298 K. Calculate Ea.
Consider a certain reaction \[\ce{A -> Products}\] with k = 2.0 × 10−2 s−1. Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100 s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L−1.
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
Match the statements given in Column I and Column II
| Column I | Column I | |
| (i) | Catalyst alters the rate of reaction | (a) cannot be fraction or zero |
| (ii) | Molecularity | (b) proper orientation is not there always |
| (iii) | Second half life of first order reaction | (c) by lowering the activation energy |
| (iv) | `e^((-E_a)/(RT)` | (d) is same as the first |
| (v) | Energetically favourable reactions (e) total probability is one are sometimes slow | (e) total probability is one |
| (vi) | Area under the Maxwell Boltzman curve is constant | (f) refers to the fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than activation energy |
Total number of vibrational degrees of freedom present in CO2 molecule is
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change ΔE during the reaction is - 20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is ______.
