Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe how does the enthalpy of reaction remain unchanged when a catalyst is used in the reaction.
Solution
A catalyst is a substance which increases the speed of a reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change.
To “intermediate complex formation theory” reactants first combine with the catalyst to form an intermediate complex which is short-lived and decomposes to form the products and regenerating the catalyst.
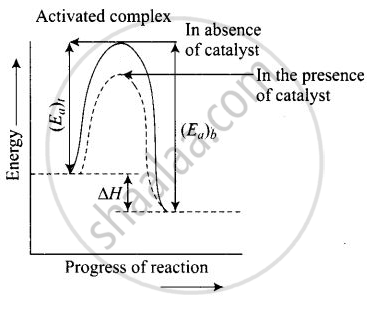
The intermediate formed has much lower potential energy than the intermediate complex formed between the reactants in the absence of the catalyst.
Thus, the presence of catalyst lower the potential energy barrier and the reaction follows a new alternate pathway which require less activation energy. We know that, the lower the activation energy, the faster is the reaction because more reactant molecules can cross the energy barrier and change into products.
Enthalpy, AH is a state function. Enthalpy of reaction, i.e., difference in energy between reactants and product is constant, which is clear from potential energy diagram.
Potential energy diagram of catalysed reaction is given as
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For a reaction
\[\ce{2H2O2->[I^-][Alkaline medium]2H2O + O2}\]
The Proposed mechanism is given below:
(1) H2O2+I- → H2O+IO-(slow)
(2) H2O2+IO-→H2O+I-+O2(fast)
(i) Write the rate law for the reaction.
(ii) Write the overall order of a reaction.
(iii) Out of steps(1) and (2), which one is the rate-determining step?
Which of the following statements regarding catalyst is FALSE?
____________ is used as a catalyst for the following reaction:
\[\ce{CO + \underset{\text{(Steam)}}{H2O} ⇌ CO2 + H2}\]
In the manufacture of ammonia by Haber's process, Al2O3 does not act as a catalyst but increases the activity of the catalyst. The role of Al2O3 can be best described as ____________.
Which of the following is a character of catalyst?
For a certain reaction large fraction of molecules has energy more than the threshold energy, yet the rate of reaction is very slow. Why?
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | Diamond | (a) short interval of time |
| (ii) | Instantaneous rate | (b) ordinarily rate of conversion is imperceptible |
| (iii) | Average rate | (c) long duration of time |
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | Mathematical expression for rate of reaction | (a) rate constant |
| (ii) | Rate of reaction for zero order reaction is equal to | (b) rate law |
| (iii) | Units of rate constant for zero order reaction is same as that of | (c) order of slowest step |
| (iv) | Order of a complex reaction is determined by | (d) rate of a reaction |
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when a catalyst is added.
For the reaction 3A `rightarrow` 2B, rate of reaction `+ (d[B])/(dt)` is equal to ______.
