Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
All energetically effective collisions do not result in a chemical change. Explain with the help of an example.
Solution
Only effective collision leads to the formation of products. It means that collisions in which molecules collide with sufficient kinetic energy (called threshold energy = activation energy + energy possessed by reacting species). And proper orientation lead to a chemical change because it facilitates the breaking of old bonds between (reactant) molecules and formation of the new ones, i.e., in products. e.g., formation of methanol from bromomethane depends upon the orientation of the reactant molecules.
\[\ce{CH3Br + OH^{-} -> CH3OH + Br^{-}}\]
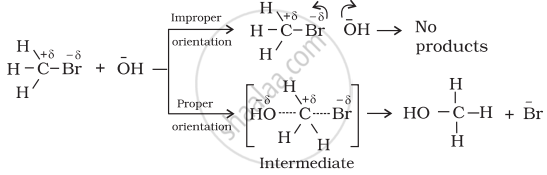
The proper orientation of reactant molecules lead to bond formation whereas improper orientation makes them simply back and no products are formed.
To account to effective collisions, another factor P (probability or steric factor) is introduced `K = Ae^((-Ea)/(RT))`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The Arrhenius equation is_________________ .
(a)`k=Ae^(RT/E_a)`
(b)`A=ke^(-E_a/(RT))`
(c)`k=Ae^(-(RT)/E_a)`
(d)`k=Ae^(-E_a/(RT))`
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(more than, primary, cathode, Lucas reagent, two, four, less than, Grignard’s reagent, tertiary anode, zero, equal to, three)
A mixture of conc. HCl and anhydrous ZnCl2 is called _______ which shows maximum reactivity with _________ alcohol.
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by ____________.
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the collison theory of chemical reaction?
Which of the following statements are applicable to a balanced chemical equation of an elementary reaction?
(i) Order is same as molecularity.
(ii) Order is less than the molecularity.
(iii) Order is greater than the molecularity.
(iv) Molecularity can never be zero.
For a reaction A + B `->` Products, the rate law is — Rate = k [A][B]3/2 Can the reaction be an elementary reaction? Explain.
Assertion: All collision of reactant molecules lead to product formation.
Reason: Only those collisions in which molecules have correct orientation and sufficient kinetic energy lead to compound formation.
For the decomposition of hydrogen iodide at 127°C, the fraction of molecules having energy equal to or greater than activation energy can be given as ______.
For a reaction, given below is the graph of ln k vs `1/"T"`. The activation energy for the reaction is equal to ______ cal mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given : R = 2 cal K-1 mol-1)

Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
| When two solutions are separated by a semi-permeable membrane, the solvent molecules move from a solution of lower molar concentration to a solution of higher molar concentration through osmosis. |
- Samar removed the outer hard shell of two different eggs while cooking at home. He then placed one egg in pure water and the other egg in a saturated solution of sucrose. What change is he likely to observe in the eggs after a few hours?
- Which solution, hypertonic or hypotonic, has a higher amount of solute in same quantity of solution?
- A 5% aqueous solution of glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol-1) is isotonic with 1.66 % aqueous solution of urea. Calculate the molar mass of urea.
