Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
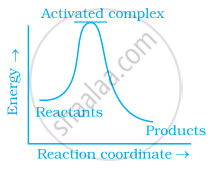
(b)
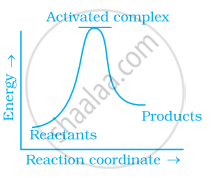
(c)
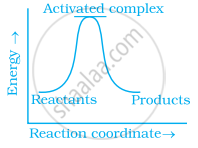
पर्याय
(a) only
(b) only
(c) only
(a) and (b)
उत्तर
(a) only
Explanation:
Exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which the enthalpy change is negative and energy is released in the form of light and heat.
As we all know, ΔH is negative.
Activation energy (forward reaction) – (backward reaction)
(Forward reaction) – Ea (backward reaction)
The product's exothermic energy exceeds the activation energy of the reactant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 × 10−5 s−1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ/mol, what will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
The decomposition of a hydrocarbon has value of rate constant as 2.5×104s-1 At 27° what temperature would rate constant be 7.5×104 × 3 s-1if energy of activation is 19.147 × 103 J mol-1 ?
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ______.
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example.
Match the statements given in Column I and Column II
| Column I | Column I | |
| (i) | Catalyst alters the rate of reaction | (a) cannot be fraction or zero |
| (ii) | Molecularity | (b) proper orientation is not there always |
| (iii) | Second half life of first order reaction | (c) by lowering the activation energy |
| (iv) | `e^((-E_a)/(RT)` | (d) is same as the first |
| (v) | Energetically favourable reactions (e) total probability is one are sometimes slow | (e) total probability is one |
| (vi) | Area under the Maxwell Boltzman curve is constant | (f) refers to the fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than activation energy |
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
The activation energy of one of the reactions in a biochemical process is 532611 J mol–1. When the temperature falls from 310 K to 300 K, the change in rate constant observed is k300 = x × 10–3 k310. The value of x is ______.
[Given: ln 10 = 2.3, R = 8.3 J K–1 mol–1]
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
