Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The decomposition of a hydrocarbon has value of rate constant as 2.5×104s-1 At 27° what temperature would rate constant be 7.5×104 × 3 s-1if energy of activation is 19.147 × 103 J mol-1 ?
उत्तर
log `K_2/K_1= Ea /(2.303 R) [(T_2 - T_1)/(T_1T_2)]`
`T_1 -> 300k-> 2.5 xx 10^4 s^-2 → K_2`
`T_1 -> 300k-> 2.5 xx 10^4 s^-2 → K_2`
log `(7.5xx10^4(T-300))/(19.15 (300T))`
⇒ `0.477/1000 xx 300T = (T-300)1000`
⇒ 143T = 1000T - 300000
⇒ 300000 = 1000T - 143T
= 857 T
`T = 300000/857 = 350 K`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 × 10−2 to 4 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Predict the main product of the following reactions: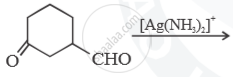
The reaction between \[\ce{H2(g)}\] and \[\ce{O2(g)}\] is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
Match the statements given in Column I and Column II
| Column I | Column I | |
| (i) | Catalyst alters the rate of reaction | (a) cannot be fraction or zero |
| (ii) | Molecularity | (b) proper orientation is not there always |
| (iii) | Second half life of first order reaction | (c) by lowering the activation energy |
| (iv) | `e^((-E_a)/(RT)` | (d) is same as the first |
| (v) | Energetically favourable reactions (e) total probability is one are sometimes slow | (e) total probability is one |
| (vi) | Area under the Maxwell Boltzman curve is constant | (f) refers to the fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than activation energy |
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
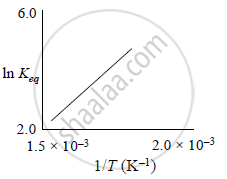
The reaction must be:
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
