Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The decomposition of a hydrocarbon has value of rate constant as 2.5×104s-1 At 27° what temperature would rate constant be 7.5×104 × 3 s-1if energy of activation is 19.147 × 103 J mol-1 ?
Solution
log `K_2/K_1= Ea /(2.303 R) [(T_2 - T_1)/(T_1T_2)]`
`T_1 -> 300k-> 2.5 xx 10^4 s^-2 → K_2`
`T_1 -> 300k-> 2.5 xx 10^4 s^-2 → K_2`
log `(7.5xx10^4(T-300))/(19.15 (300T))`
⇒ `0.477/1000 xx 300T = (T-300)1000`
⇒ 143T = 1000T - 300000
⇒ 300000 = 1000T - 143T
= 857 T
`T = 300000/857 = 350 K`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10−2 to 8 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea). (log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
Define activation energy.
The chemical reaction in which reactants require high amount of activation energy are generally ____________.
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
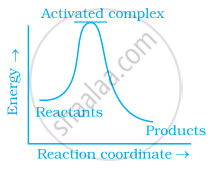
(b)
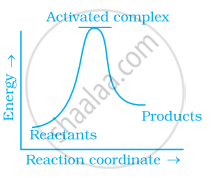
(c)
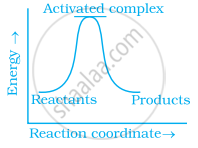
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as ______.
The slope of Arrhenius Plot `("In" "k" "v"//"s" 1/"T")` of first-order reaction is −5 × 103 K. The value of Ea of the reaction is. Choose the correct option for your answer. [Given R = 8.314 JK−1mol−1]
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
