Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10−2 to 8 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea). (log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Solution
Given:
k1 = 4 × 10−2
k2 = 8 × 10−2
T1 = 300 K
T2 = 310 K
Solution:
`log(k_2/k_1)=E_a/(2.303R)[(T_2-T_1)/(T_1T_2)]`
`log((8xx10^(-2)|)/(4xx10^(-2)))=E_a/(2.303R)[(T_2-T_1)/(T_1T_2)]`
`0.301= E_a/(2.303xx 8.314JK^(-1)mol^(-1))[(310-300)/(310xx300)]`
`E_a=(0.301 × 2.303 × 8.314 × 93000)/10`
Ea = 53598.5 J
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 × 10−5 s−1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ/mol, what will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
The rate of chemical reaction becomes double for every 10° rise in temperature because of ____________.
Consider figure and mark the correct option.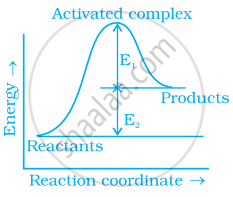
Oxygen is available in plenty in air yet fuels do not burn by themselves at room temperature. Explain.
Match the statements given in Column I and Column II
| Column I | Column I | |
| (i) | Catalyst alters the rate of reaction | (a) cannot be fraction or zero |
| (ii) | Molecularity | (b) proper orientation is not there always |
| (iii) | Second half life of first order reaction | (c) by lowering the activation energy |
| (iv) | `e^((-E_a)/(RT)` | (d) is same as the first |
| (v) | Energetically favourable reactions (e) total probability is one are sometimes slow | (e) total probability is one |
| (vi) | Area under the Maxwell Boltzman curve is constant | (f) refers to the fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than activation energy |
The slope of Arrhenius Plot `("In" "k" "v"//"s" 1/"T")` of first-order reaction is −5 × 103 K. The value of Ea of the reaction is. Choose the correct option for your answer. [Given R = 8.314 JK−1mol−1]
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
What happens to the rate constant k and activation energy Ea as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased? Justify.
