Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2014-2015
Date: March 2015
Advertisements
Write a method by which lyophobic colloids can be coagulated.
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
What is the formula of a compound in which the element Y forms hcp lattice and atoms of X occupy 2/3rd of tetrahedral voids?
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Out of white phosphorus and red phosphorus, which one is more reactive and why?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:
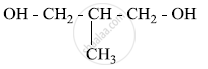
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair and why?
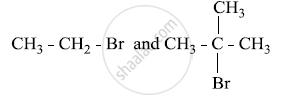
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Why do gases always tend to be less soluble in liquids as the temperature is raised?
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
State Raoult’s law for the solution containing volatile components
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Write two differences between an ideal solution and a non-ideal solution.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution:
Na+(aq) + e− ⟶ Na (s) E0 = 2.71 V
H+(aq) + e− ⟶ `1/2` H2 (g) E0 = 0.00 V
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E0) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Why does the cell potential of mercury cell remain constant throughout its life?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Why do the transition elements have higher enthalpies of atomisation?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
In 3d series (Sc to Zn), which element has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation and why?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex: [Co(NH3)5 (NO2)](NO3)2
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Using IUPAC norms, write the formula for the following:
Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:

Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Name the reagents used in the following reactions:
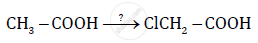
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Advertisements
Calculate the amount of CaCl2 (molar mass = 111 g mol−1) which must be added to 500 g of water to lower its freezing point by 2 K, assuming CaCl2 is completely dissociated. (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol−1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
An element with density 10 g cm−3 forms a cubic unit cell with edge length of 3 × 10−8 cm. What is the nature of the cubic unit cell if the atomic mass of the element is 81 g mol−1?
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Calculate emf of the following cell at 25°C:
\[\ce{Sn/Sn^2+ (0.001 M) || H+ (0.01 M) | H2_{(g)} (1 bar) | Pt_{(s)}}\]
Given: \[\ce{E^\circ(Sn^2+/sn) = -0.14 V, E^\circ H+/H2 = 0.00 V (log 10 = 1)}\]
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Give reasons for the following observations:
Physisorption decreases with increase in temperature.
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Give reasons for the following observations: Addition of alum purifies the water
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Give reasons for the following observations:
Brownian movement provides stability to the colloidal solution.
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Name the method used for the refining of zirconium.
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What is the role of CO in the extraction of Iron?
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Reduction of metal oxide to metal becomes easier if the metal obtained is in liquid state. Why?
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
How would you account for the following:
The chemistry of actinoids is more complicated as compared to lanthanoids.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
How would you account for the following: Transition metals form complex compounds.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete the following equation:
\[\ce{2MnO4- + 6H+ + 5NO2- ->}\]
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Draw the geometrical isomers of complex \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]+}\].
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δ0 > P.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
[NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic, while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
How do you convert the following: Prop-1-ene to 1-fluoropropane
Chapter:
How do you convert the following: Chlorobenzene to 2-chlorotoluene
Chapter:
How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to propanenitrile
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write the main products when n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write the main products when
2, 4, 6-trinitrochlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the main products when methyl chloride is treated with AgCN.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Give reasons for the following:
o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Give reasons for the following: Butan-1-ol has a higher boiling point than diethyl ether.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Give reasons for the following:
(CH3)3C–O–CH3 on reaction with HI gives (CH3)3C–I and CH3–OH as the main products and not (CH3)3C–OH and CH3–I.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Predict the products of the following reactions:
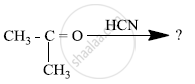
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Predict the products of the following reactions:
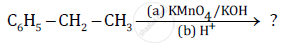
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Predict the products of the following reactions:
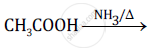
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Advertisements
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: Nylon-6
Chapter:
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: Novolac
Chapter:
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following polymers: Buna-N
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Which one of the following is a polysaccharide:
Starch, Maltose, Fructose, Glucose
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
What is the difference between native protein and denatured protein?
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Write the name of the vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Seeing the growing cases of diabetes and depression among young children, Mr Lugani, the principal of one reputed school, organised a seminar in which he invites parents and principals. They all resolved this issue by strictly banning junk food in schools and introducing healthy snacks and drinks like soup, lassi, milk etc. in school canteens. They also decided to make compulsory half an hour of daily physical activities for the students in the health survey in most of the school and discovered a tremendous improvement in the health of the students
After reading the above passage, answer the following questions:
(i) What are the values (at least two) displayed by Mr Lugani?
(ii) As a student, how can you spread awareness about this issue?
(iii) What are antidepressant drugs? Give an example.
(iv) Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
Write the chemical equation involved in the following reaction:
Hoffmann-bromamide degradation reaction
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Illustrate the following reaction giving suitable example in each case: Diazotisation
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Illustrate the following reaction giving suitable example in each case:Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Distinguish between the following pairs of compounds: Aniline and N-methylaniline
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride `(C_6H_5N_2^(+)Cl^-)`reacts with the following reagents:
CuCN/KCN
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride `(C_6H_5N_2^(+)Cl^-)`reacts with the following reagents:
H2O
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride `(C_6H_5N_2^(+)Cl^-)`reacts with the following reagents:
CH3CH2OH
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Arrange the following:
Aniline, p-nitroaniline, p-methylaniline - in the increasing order of their basic strength
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10−2 to 8 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea). (log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
For a reaction A + B ⟶ P, the rate is given by
Rate = k [A] [B]2
What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
A first order reaction takes 23.1 minutes for 50% completion. Calculate the time required for 75% completion of this reaction.
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Account for the following: Interhalogens are more reactive than pure halogens.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Account for the following:
N2 is less reactive at room temperature.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Account for the following: Reducing character increases from NH3 to BiH3.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Draw the structures of the following: H4P2O7 (Pyrophosphoric acid)
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Draw the structures of the following molecules: XeF4
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
which poisonous gas is evolved when white phosphorus is heated with conc. NaOH solution? Write the chemical equation involved.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Which noble gas has the lowest boiling point?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent than chlorine. Why?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
What happens when
H3PO3 is heated ?
Write the reactions involved.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Complete the equation
PbS + O3 ⟶
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2014 - 2015
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2015 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
