Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
[NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic, while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic number of Ni = 28)
Why is [NiCl4]2– paramagnetic but [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic? (At. nos. : Cr = 24, Co = 27, Ni = 28)
[NiCl4]2− is paramagnetic, while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why?
Solution 1
In [Ni(CO)4], nickel is in zero oxidation state, whereas in [NiCl4]2− it is in +2 oxidation state. In the presence of CO ligand, the unpaired d-electrons of nickel get paired, but Cl– being a weak ligand is not able to pair the unpaired electrons. Hence, there is no unpaired electron present in [Ni(CO)4], so it is diamagnetic and due to the presence of unpaired electrons in [NiCl4]2−, it is paramagnetic.
Solution 2
In [NiCl4]2−, the oxidation state of Ni is +2. Chloride is a weak field ligand and does not cause pairing up of electrons against the Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. As a result, two unpaired electrons are present in the valence d-orbitals of Ni, which impart paramagnetic character to the complex. On the other hand, carbonyl is a strong field ligand and causes pairing up of electrons against the Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. As a result, no unpaired electrons are present and hence, the complex is diamagnetic.
Solution 3
[NiCl4]2− and [Ni(CO)4] both are tetrahedral. But their magnetic characters are different. This is due to difference in the nature of ligands.
Ni+2 = [Ar] 4s03d8
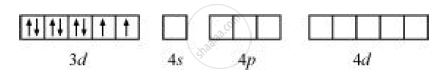
Ni+2 has 2 unpaired electrons hence, this complex is paramagnetic.
In Ni(CO)4, Ni is in the zero oxidation state i.e., it has a configuration of 3d84s2.
Ni = [Ar] 4s2 3d8
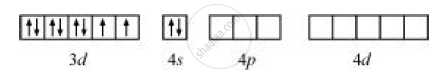
But CO is a strong field ligand. Therefore, it causes the pairing of unpaired 3d electrons. Also, it causes the 4s electrons to shift to the 3d orbital, thereby giving rise to sp3 hybridization. Since no unpaired electrons are present in this case, [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic.
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their questions.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
On the basis of valence bond theory explain the nature of bonding in [CoF6]3 ion.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Mn(CN)6]^{3-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[Cr(H2O)6]^{3+}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complexes given below:
\[\ce{[FeCl6]^{4-}}\]
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour.
(iv) Spin only magnetic moment value.
The type of hybridization involved in Octahedral complexes is ______.
In a coordination entity, the electronic configuration of the central metal ion is t2g3 eg1
Is the coordination compound a high spin or low spin complex?
When the hybridization state of carbon changes from sp3 to sp2 and finally to sp, the angle between hybridized orbital will
In Fe(CO)5, the Fe – C bond possesses
Valence bond theory is based on the assumption that the bonds formed between the metal ions and ligands are ______
During chemistry class, a teacher wrote \[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\] as a coordination complex ion on the board. The students were asked to find out the magnetic behaviour and shape of the complex. Pari, a student, wrote the answer paramagnetic and tetrahedral whereas another student Suhail wrote diamagnetic and square planer.
Evaluate Pari’s and Suhail’s responses.
