Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
Solution
The rate of reaction will decrease. At lower temperatures, the kinetic energy of molecules decreases thereby the collisions decrease resulting in a lowering of the rate of reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The activation energy for the reaction \[\ce{2 HI_{(g)} -> H2_{(g)} + I2_{(g)}}\] is 209.5 kJ mol−1 at 581K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
Calculate activation energy for a reaction of which rate constant becomes four times when temperature changes from 30 °C to 50 °C. (Given R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1).
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
The chemical reaction in which reactants require high amount of activation energy are generally ____________.
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ______.
During decomposition of an activated complex:
(i) energy is always released
(ii) energy is always absorbed
(iii) energy does not change
(iv) reactants may be formed
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
In respect of the eqn k = \[\ce{Ae^{{-E_a}/{RT}}}\] in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statement is correct?
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
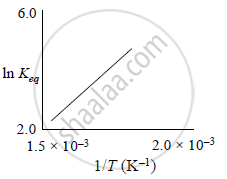
The reaction must be:
