Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
उत्तर
The rate of reaction will decrease. At lower temperatures, the kinetic energy of molecules decreases thereby the collisions decrease resulting in a lowering of the rate of reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 at various temperatures is given below:
| T/°C | 0 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| 105 × k/s−1 | 0.0787 | 1.70 | 25.7 | 178 | 2140 |
Draw a graph between ln k and `1/"T"` and calculate the values of A and Ea. Predict the rate constant at 30º and 50ºC.
In the Arrhenius equation for a first order reaction, the values of ‘A’ of ‘Ea’ are 4 x 1013 sec-1 and 98.6 kJ mol-1 respectively. At what temperature will its half life period be 10 minutes?
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1]
The rate constant of a first order reaction are 0.58 S-1 at 313 K and 0.045 S-1 at 293 K. What is the energy of activation for the reaction?
Define activation energy.
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
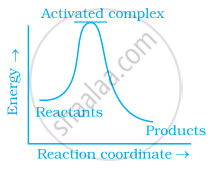
(b)
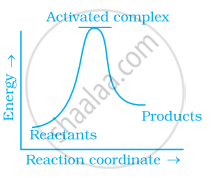
(c)
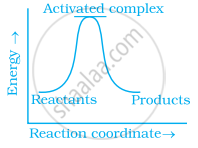
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example.
Total number of vibrational degrees of freedom present in CO2 molecule is
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
