Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The rate constant of a first order reaction are 0.58 S-1 at 313 K and 0.045 S-1 at 293 K. What is the energy of activation for the reaction?
उत्तर
Given: Rate constant k1 = 0.58 s-1
Rate constant k2 = 0.045 s-1
T1 = 313 K
T2 = 293 K
R = 8.314 J K-1mol-1
To find: Activation energy (Ea)
Formula : `log_10 "k"_2/"k"_1 = "E"_"a"/(2.303"R")[("T"_2 - "T"_1)/("T"_1"T"_2")]`
Calculation : From Formula,
`log10((0.045 "s"^-1)/(0.58 "s"^-1)) = "E"_"a"/(2.303 xx 8.314 "JK"^-1 "mol"^-1)[(293"K" - 313 "K")/(293 "K" xx 313 "K")]`
∴ log 0.0776 = `"E"_"a"/(19.147 "J" "mol"^-1)[(-20)/(293 xx 313)]`
∴ `-1.110 = "E"_"a"/19.147[(-20)/(293 xx 313)]`
∴`"E"_"a" = (-1.110 xx 19.147 xx 293 xx 313)/-20`
= 97455.34 J `"mol"^-1`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain a graphical method to determine activation energy of a reaction.
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The rate constant for the first-order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation:
`logk=14.2-(1.0xx10^4)/TK`
Calculate Ea for this reaction and rate constant k if its half-life period be 200 minutes.
(Given: R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1)
The activation energy for the reaction \[\ce{2 HI_{(g)} -> H2_{(g)} + I2_{(g)}}\] is 209.5 kJ mol−1 at 581K. Calculate the fraction of molecules of reactants having energy equal to or greater than activation energy?
The rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 × 10−5 s−1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ/mol, what will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
Consider a certain reaction \[\ce{A -> Products}\] with k = 2.0 × 10−2 s−1. Calculate the concentration of A remaining after 100 s if the initial concentration of A is 1.0 mol L−1.
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 × 103 s−1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol−1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 × 104 s−1?
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
Define activation energy.
Calculate activation energy for a reaction of which rate constant becomes four times when temperature changes from 30 °C to 50 °C. (Given R = 8.314 JK−1 mol−1).
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on Activation energy (Ea)
A first-order reaction is 50% completed in 40 minutes at 300 K and in 20 minutes at 320 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction. (Given : log 2 = 0·3010, log 4 = 0·6021, R = 8·314 JK–1 mol–1)
The rate of chemical reaction becomes double for every 10° rise in temperature because of ____________.
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by ______.
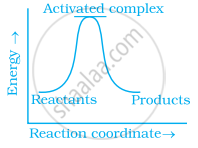
Which of the following graphs represents exothermic reaction?
(a)
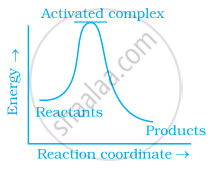
(b)
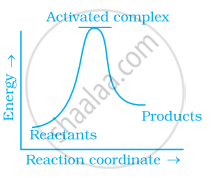
(c)
Oxygen is available in plenty in air yet fuels do not burn by themselves at room temperature. Explain.
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example.
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
Total number of vibrational degrees of freedom present in CO2 molecule is
In respect of the eqn k = \[\ce{Ae^{{-E_a}/{RT}}}\] in chemical kinetics, which one of the following statement is correct?
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
The slope of Arrhenius Plot `("In" "k" "v"//"s" 1/"T")` of first-order reaction is −5 × 103 K. The value of Ea of the reaction is. Choose the correct option for your answer. [Given R = 8.314 JK−1mol−1]
The equation k = `(6.5 xx 10^12 "s"^(-1))"e"^(- 26000 " K"//"T")` is followed for the decomposition of compound A. The activation energy for the reaction is ______ kJ mol-1. (Nearest integer) (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1)
An exothermic reaction X → Y has an activation energy 30 kJ mol-1. If energy change ΔE during the reaction is - 20 kJ, then the activation energy for the reverse reaction in kJ is ______.
A schematic plot of ln Keq versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
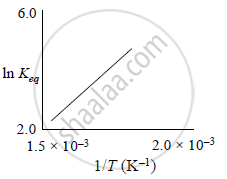
The reaction must be:
It is generally observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 10oC rise in temperature. If the generalisation holds true for a reaction in the temperature range of 298K to 308K, what would be the value of activation energy (Ea) for the reaction?
