Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The rate constant for the decomposition of hydrocarbons is 2.418 × 10−5 s−1 at 546 K. If the energy of activation is 179.9 kJ/mol, what will be the value of pre-exponential factor?
उत्तर
k = 2.418 × 10−5 s−1
T = 546 K
Ea = 179.9 kJ mol−1
According to the Arrhenius equation,
log A = log k + `"E"_"a"/(2.303 "RT")`
= log (2.418 × 10−5) + `179.9/(2.303 xx 8.314 xx 10^(-3) xx 546)`
= (−5 + 0.3834) + 17.2081
= 12.5924 s−1
or, A = Antilog (12.5924) s−1 = 3.902 × 1012 s−1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the reaction
`3I_((aq))^-) +S_2O_8^(2-)->I_(3(aq))^-) + 2S_2O_4^(2-)`
At particular time t, `(d[SO_4^(2-)])/dt=2.2xx10^(-2)"M/s"`
What are the values of the following at the same time?
a. `-(d[I^-])/dt`
b. `-(d[S_2O_8^(2-)])/dt`
c. `-(d[I_3^-])/dt`
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 × 10−2 to 4 × 10−2 when the temperature changes from 300 K to 310 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
What will be the effect of temperature on rate constant?
The decomposition of hydrocarbon follows the equation k = `(4.5 xx 10^11 "s"^-1) "e"^(-28000 "K"//"T")`
Calculate Ea.
The decomposition of A into product has value of k as 4.5 × 103 s−1 at 10°C and energy of activation 60 kJ mol−1. At what temperature would k be 1.5 × 104 s−1?
Explain the following terms :
Half life period of a reaction (t1/2)
The decomposition of a hydrocarbon has value of rate constant as 2.5×104s-1 At 27° what temperature would rate constant be 7.5×104 × 3 s-1if energy of activation is 19.147 × 103 J mol-1 ?
Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction. (Given : log2 = 0.3010,log 3 = 0.4771, log5 = 0.6990).
Consider figure and mark the correct option.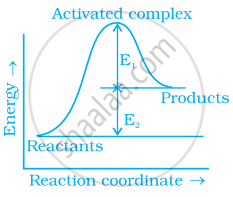
Mark the incorrect statements:
(i) Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to reaction mechanism.
(ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy.
(iii) Catalyst lowers the activation energy.
(iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change of the reaction.
The reaction between \[\ce{H2(g)}\] and \[\ce{O2(g)}\] is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature?
Why in the redox titration of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
What happens to most probable kinetic energy and the energy of activation with increase in temperature?
Total number of vibrational degrees of freedom present in CO2 molecule is
For an endothermic reaction energy of activation is Ea and enthalpy of reaction ΔH (both of there in KJ moI–1) minimum value of Ea will be
The rate constant for a reaction is 1.5 × 10–7 sec–1 at 50°C. What is the value of activation energy?
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
